We have learned that vegetables are plant or plant parts eaten as food.
What are the benefits of growing our own vegetables?
Importance of growing vegetables
Activity 1
Sharing experiences on the importance of growing vegetables.
Let us Find Out
- Why is it important to eat vegetables?
- Have you seen vegetables growing in a garden?
- Are there any benefits of growing your own vegetables?
Share with your group members.
Look at the following pictures and say what is happening in each.
A.
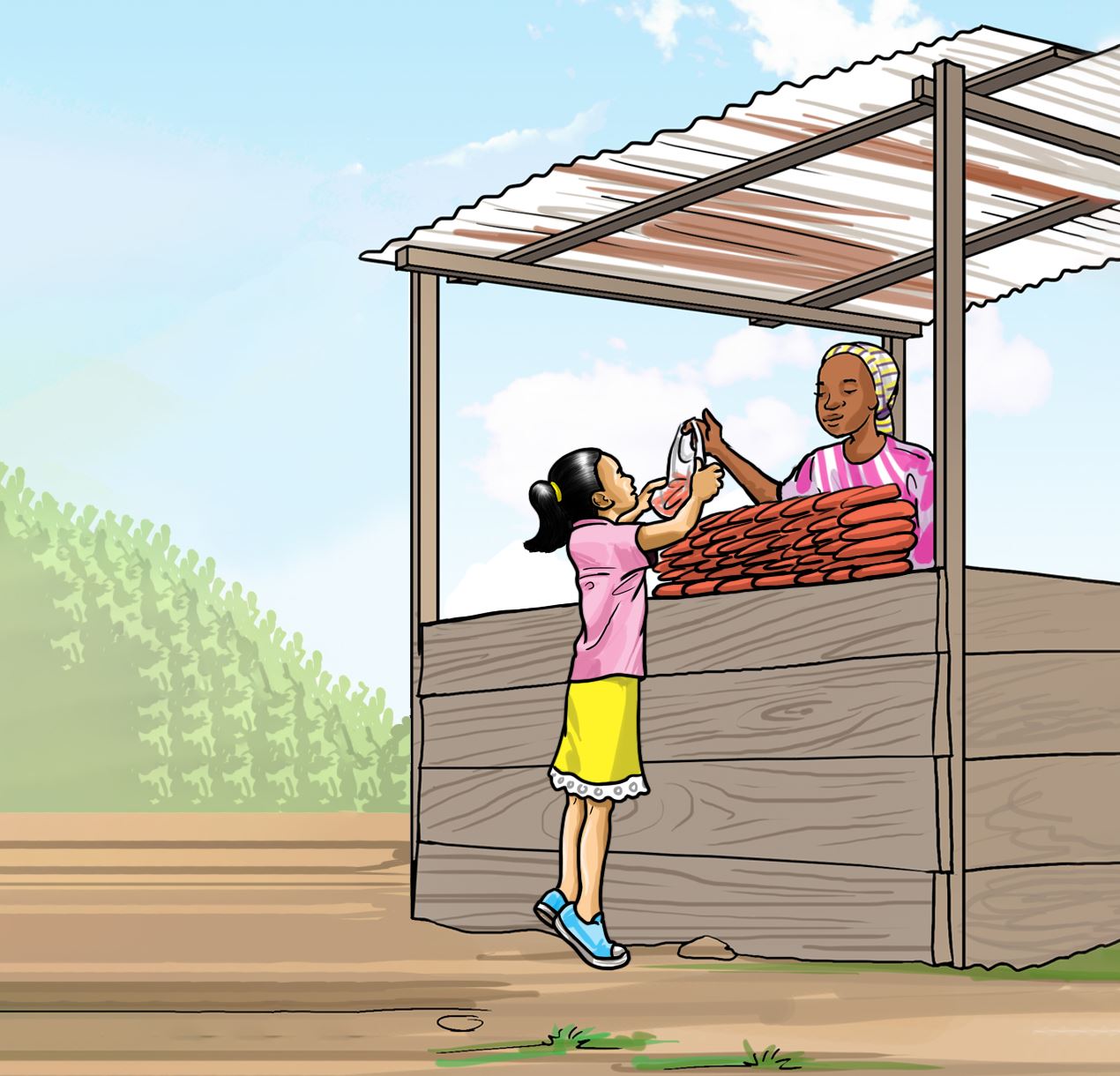

B.

Which of the two learners will save his or her parent's money?
Share how we can help our parents save money by growing our own vegetables.
Let us understand
We get vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from vegetables. They also improve digestion of food.
When we grow our own vegetables:
- We save money.
- We eat healthier vegetables because we know what has been put in them.
- We choose the type we want to grow and eat.
- We can grow them in small spaces.
- We get food security in our families.
Vegetable gardening practices
Activity 2
Sharing experiences on gardening practices of vegetables.
Let us practice
- Have you seen vegetables growing in a garden?
- What practices are needed for vegetables to do well?
- What do these practices mean; thinning, mulching and weeding?
Share with your group members.
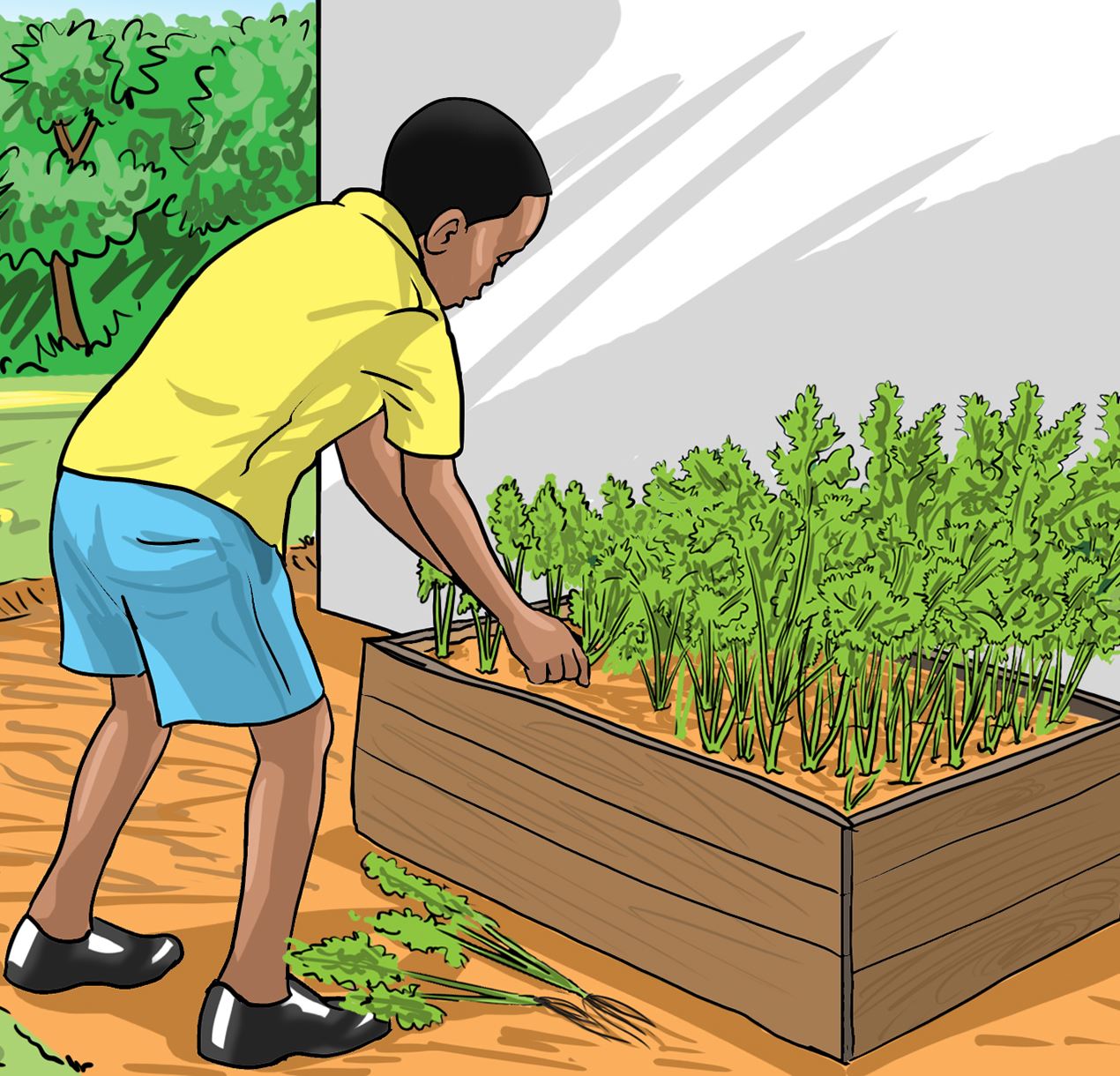
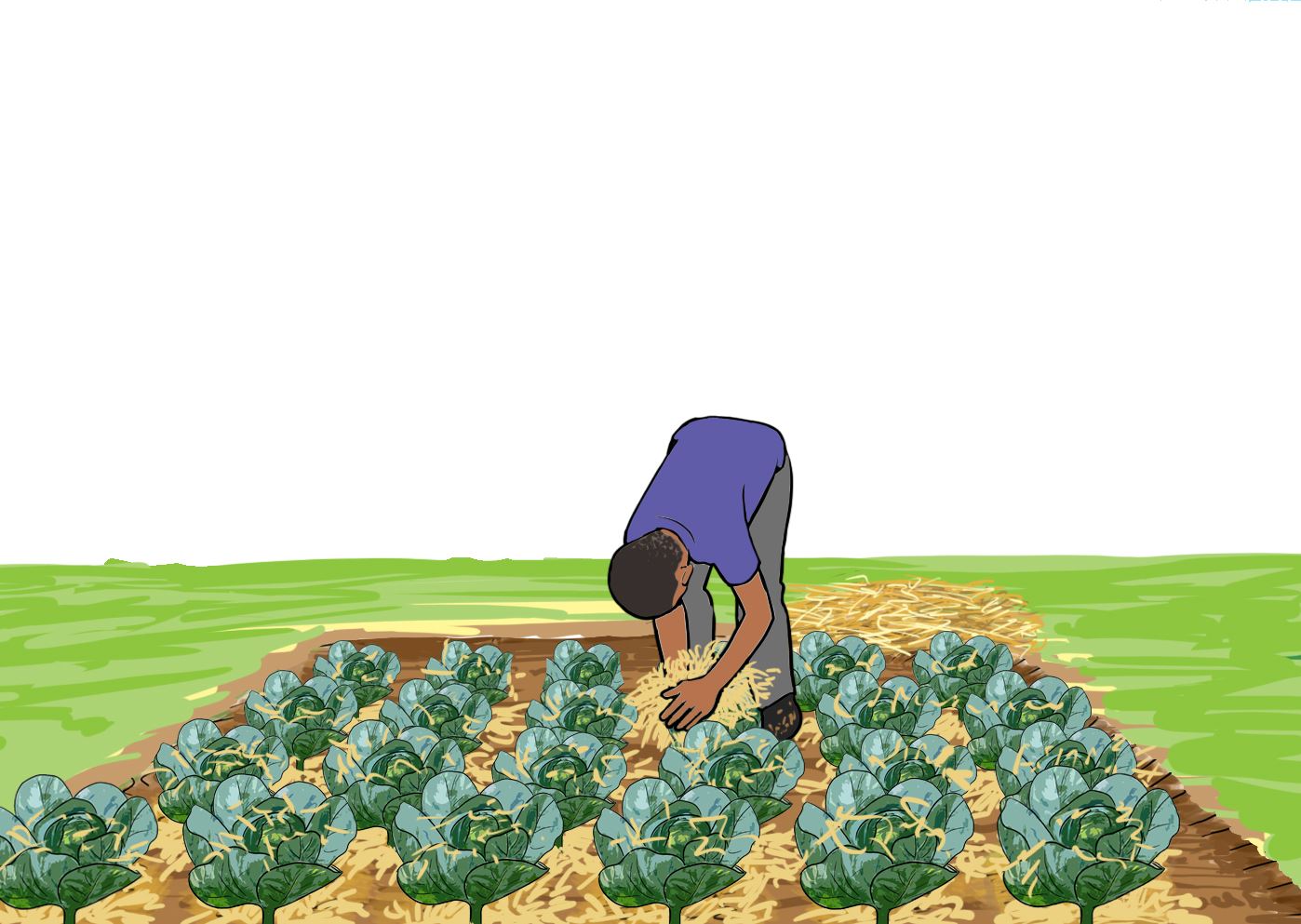
Look at the following pictures and say what the children are doing in each
A.

B.
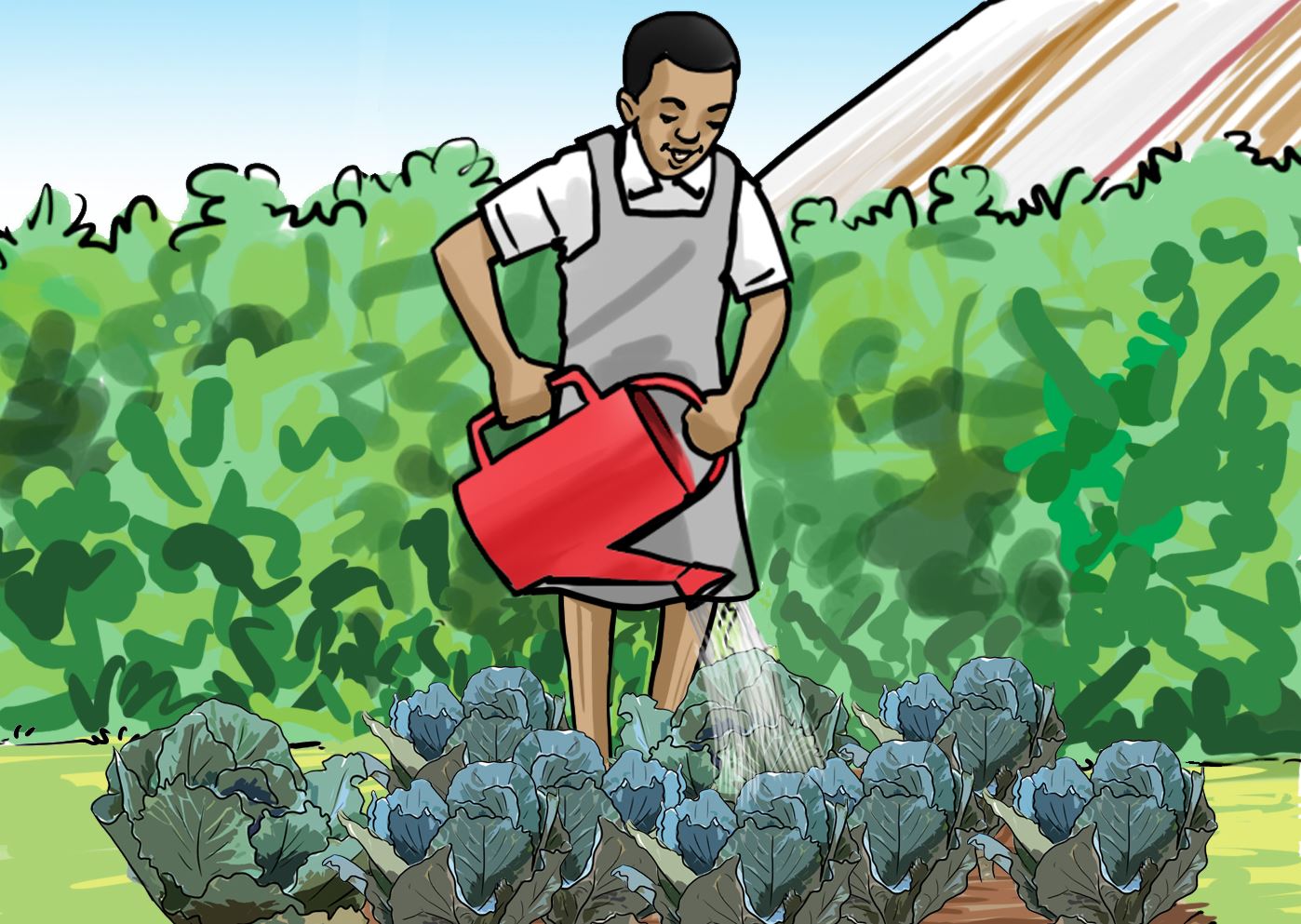

C.
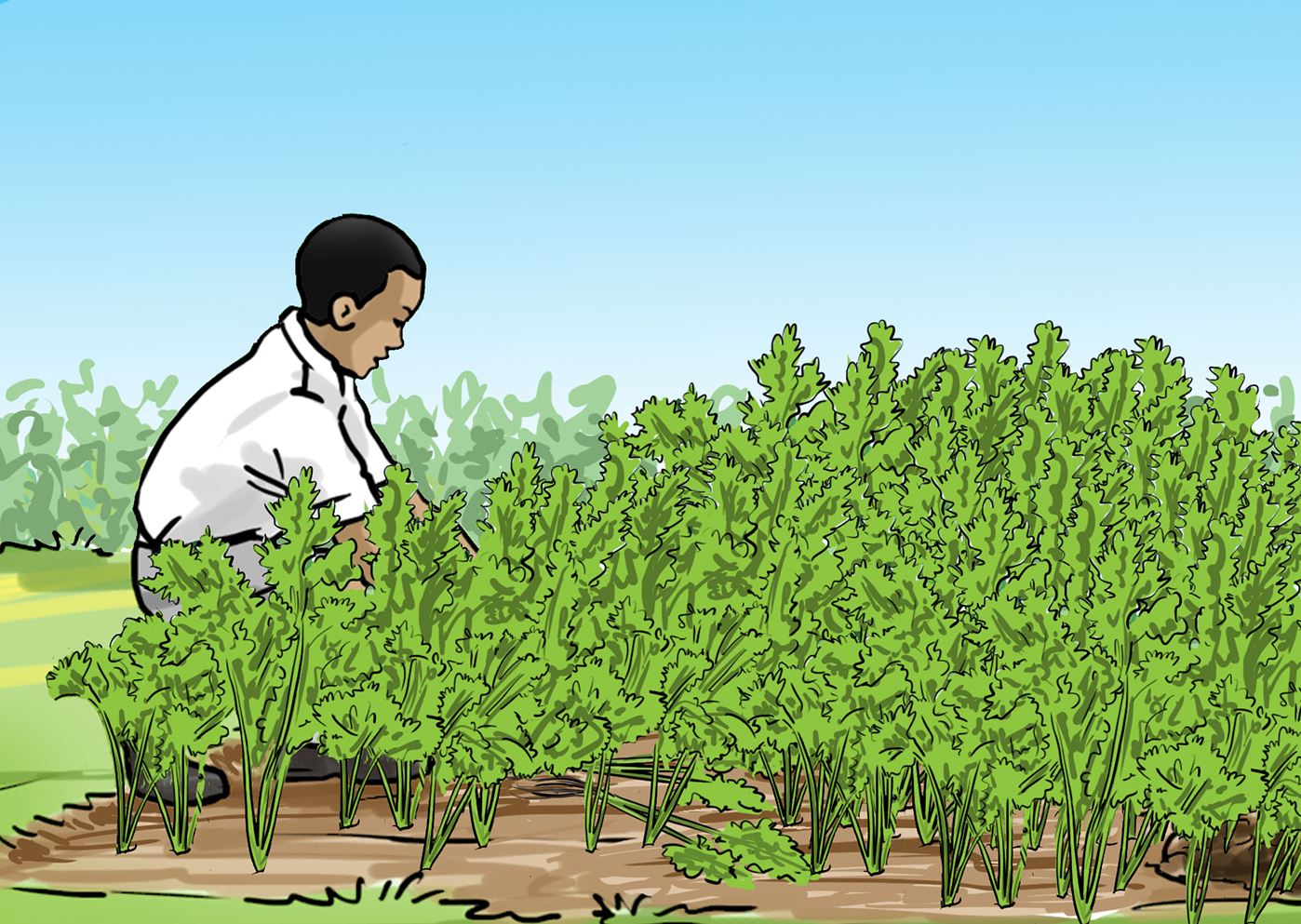

D.

Discuss in your group why each practice is done.
Let us understand
Gardening practices for vegetables include:
- Mulching – done to conserve water.
- Watering – done during dry period.
- Thinning – done to remove excess plants.
- Weeding – done to remove unwanted plants.
- Removing diseased parts of plants to control spread of diseases.
Preparing a vegetable nursery bed and sowing vegetable seeds
A nursery bed is prepared for sowing vegetable seeds.
How is a nursery bed prepared for sowing vegetable seeds?
Activity 3
Watching a video clip on how to prepare a nursery bed and sow vegetable seeds.
Let us practice
Search and watch a video clip on how to prepare a nursery bed and sow vegetable seeds into the nursery bed.
- How did you prepare the nursery bed?
- How is sowing vegetable seeds done in the nursery bed?
Share your experiences with the others in class.
Let us understand
- The place identified for the nursery bed is prepared by cultivating, breaking soil and levelling.
- Shallow drills are made on the nursery bed.
- The vegetable seeds are dropped uniformly in the shallow drills.
- The vegetable seeds are covered lightly with soil.
Activity 4
Preparing a suitable nursery bed for planting vegetables.
Let us practice
Select an area in the school that is well drained, free from shade, gently sloping and near a water source.
Working in groups
Prepare a vegetable nursery bed on the site you selected as guided by the pictures a, b, c and d.
A.

B.
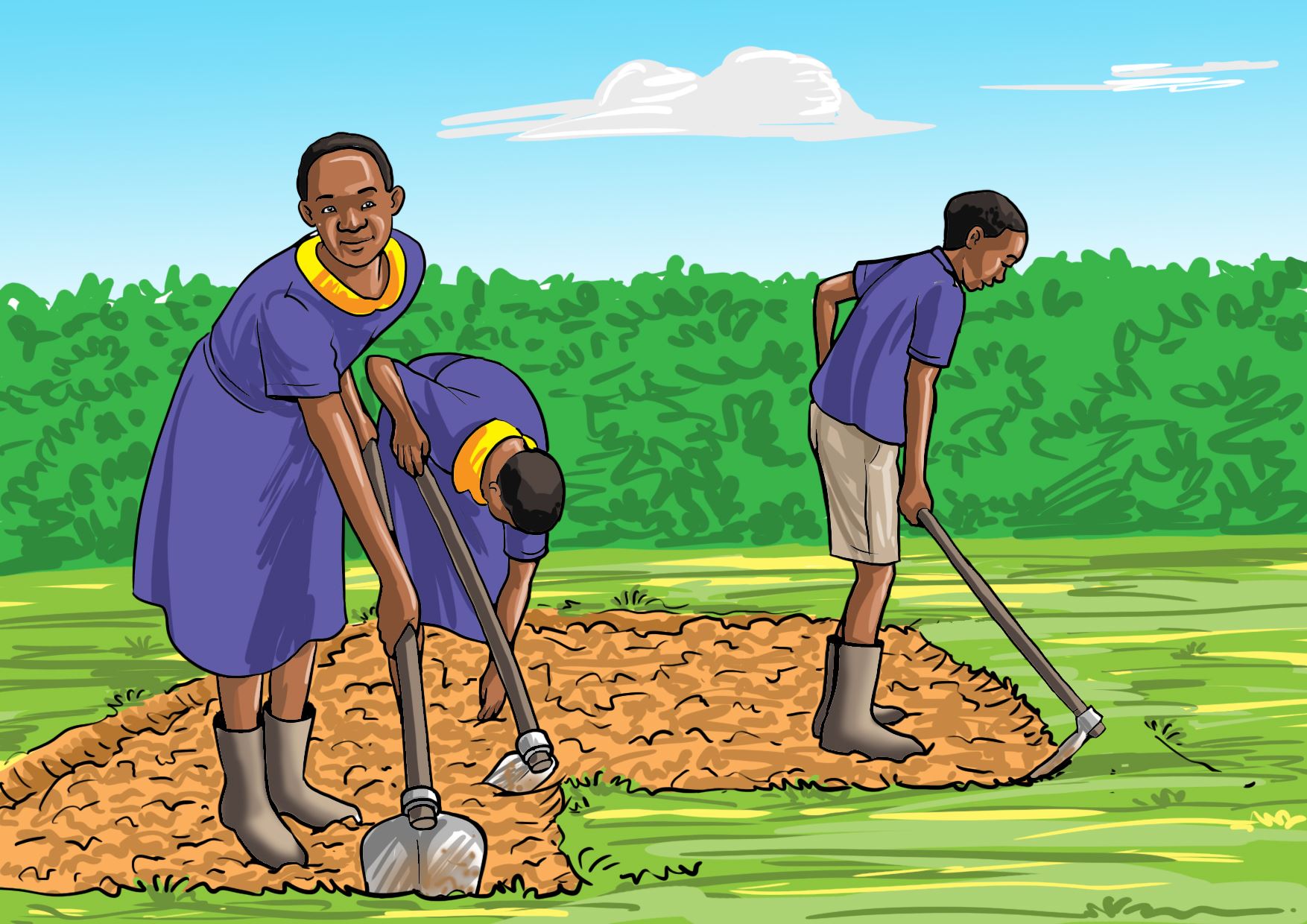

C.
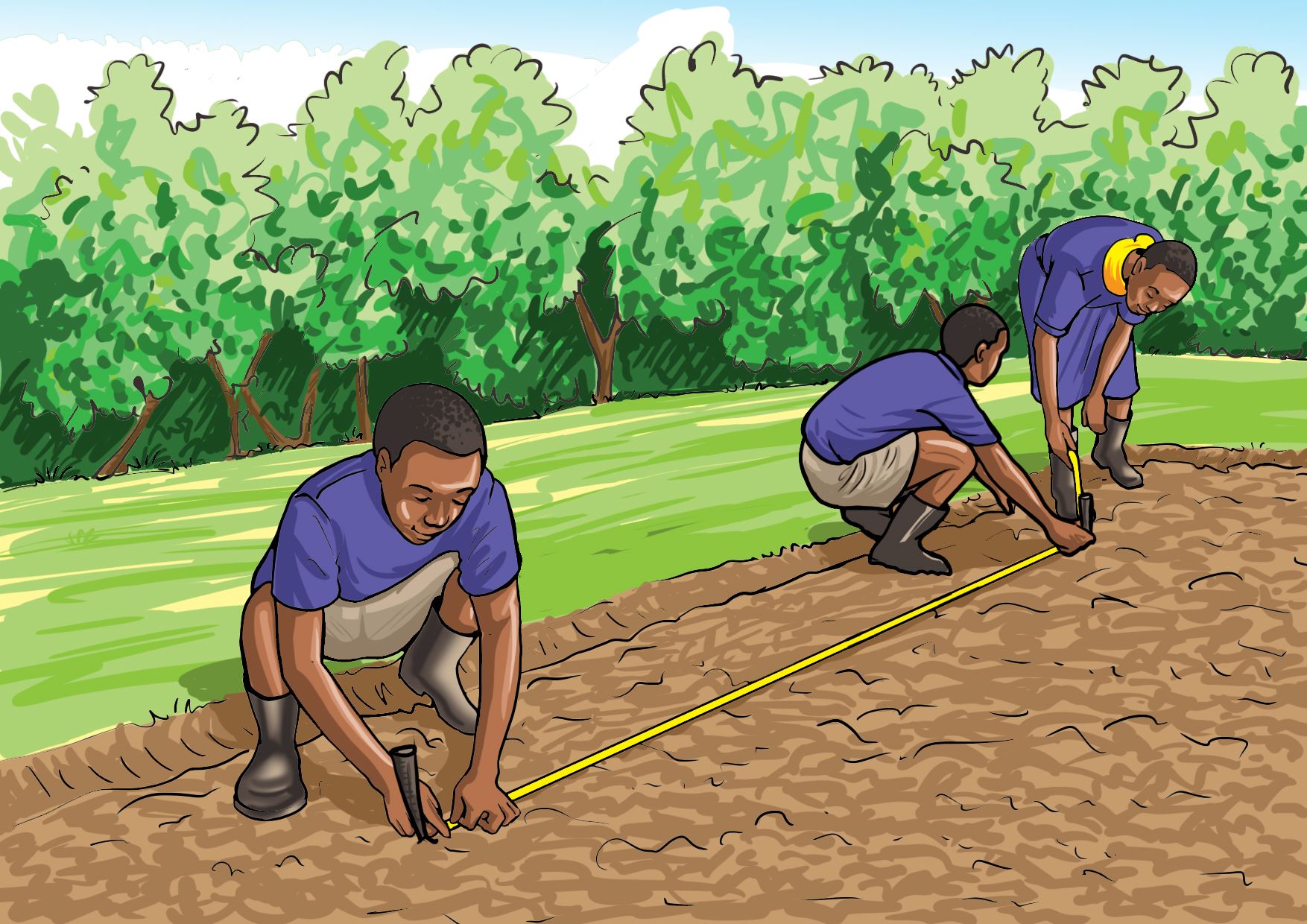

D.

Discuss with other groups, the activities you have carried out.
Let us understand
- Fine soil is needed for a suitable nursery bed.
- The nursery bed should be levelled.
How to sow vegetable seeds in a prepared nursery bed
Activity 5
Sowing vegetable seeds in the nursery bed.
Follow the activities in the pictures below on how to sow vegetable seeds. Use them to guide you to sow vegetable seeds in the nursery bed you prepared in Activity 4.
A.
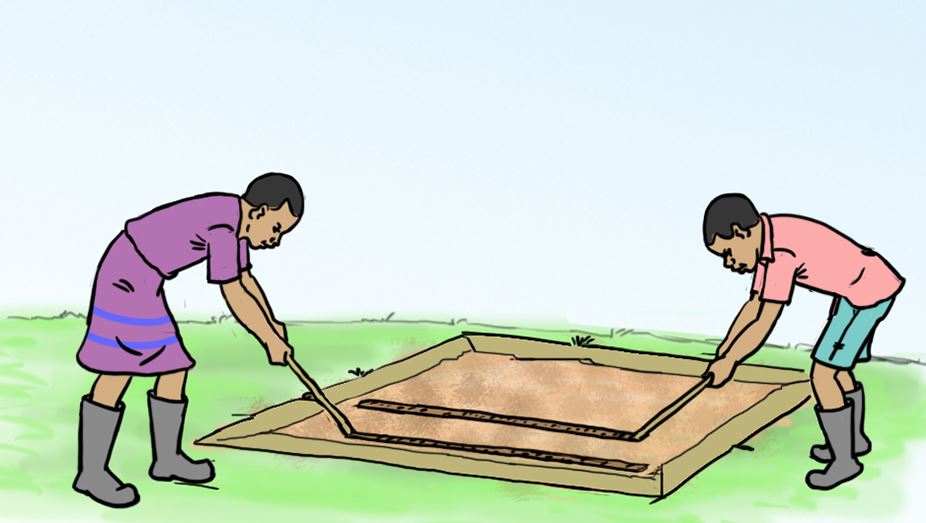
B.
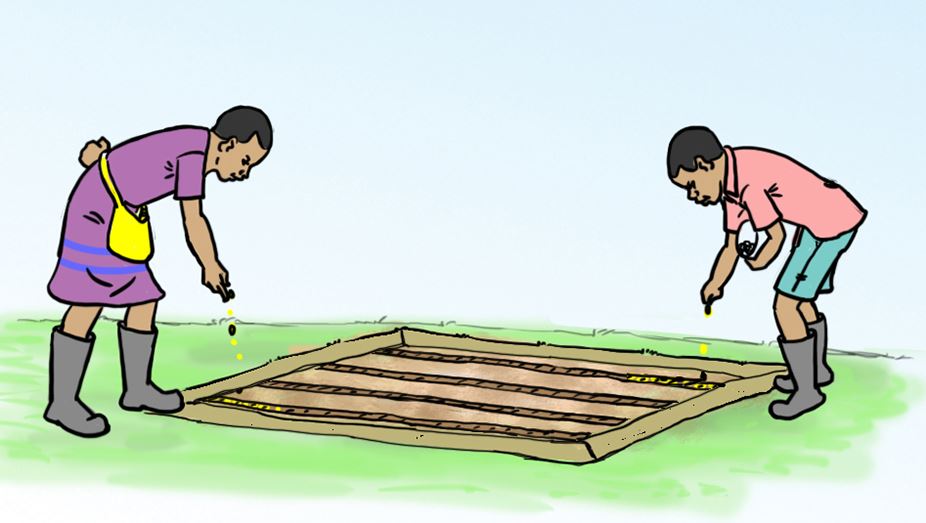
C.
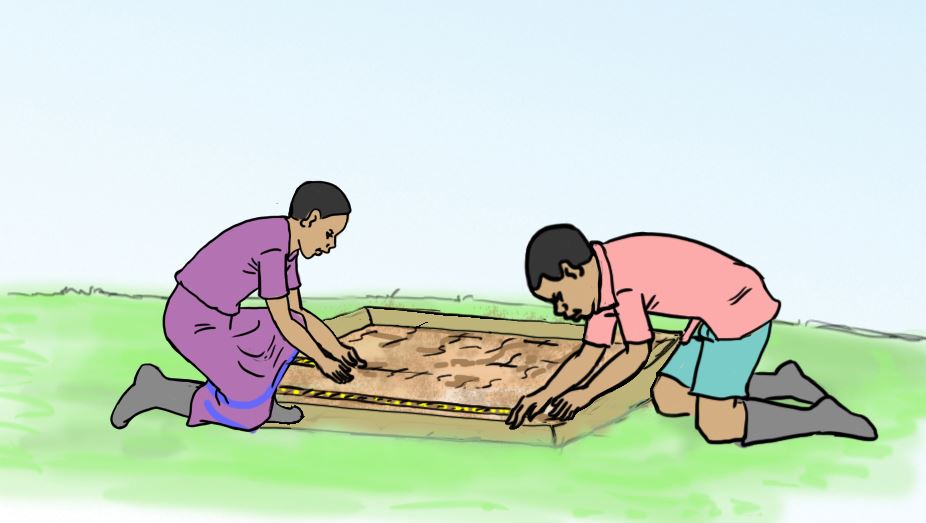

D.
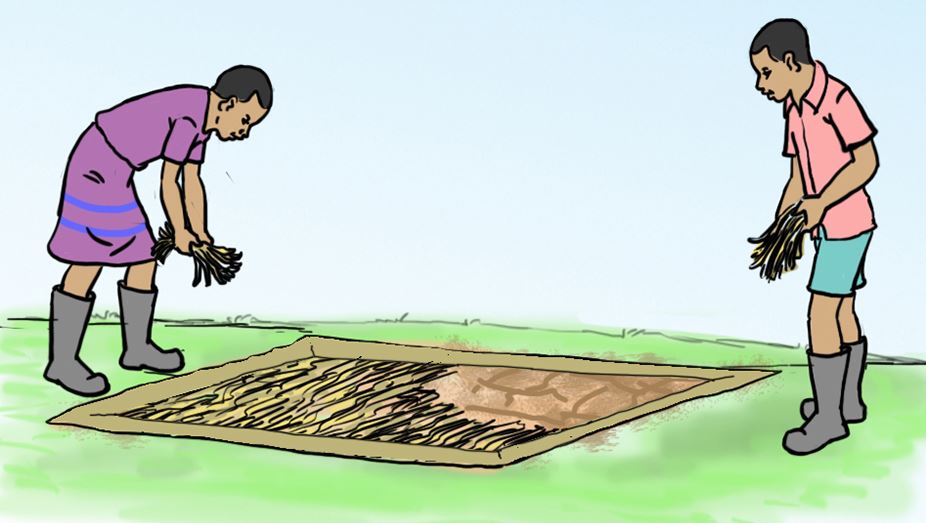

E.
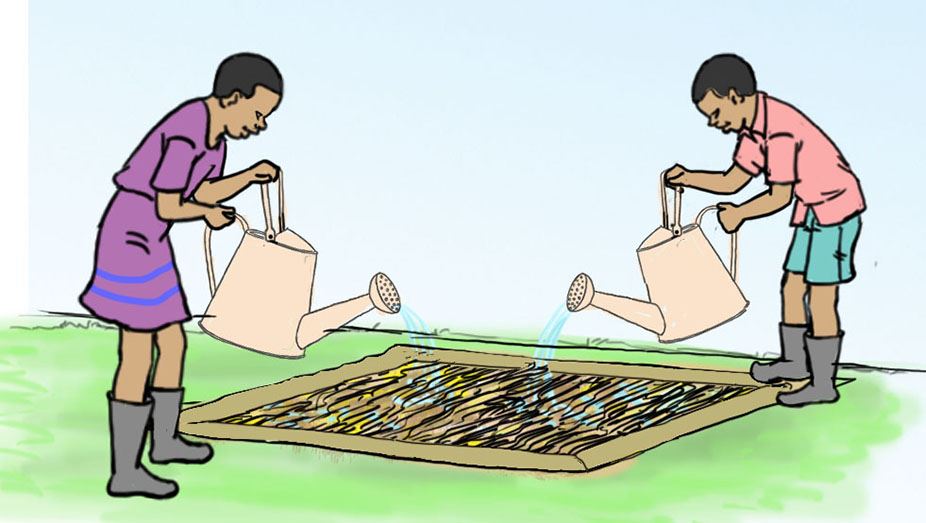

Share your experiences with the other groups.
Let us understand
- Vegetable seeds are planted in shallow furrows.
- Mulch is used to reduce loss of water from the soil.
- Mulch also prevents the seeds and the soil from being carried away by water.
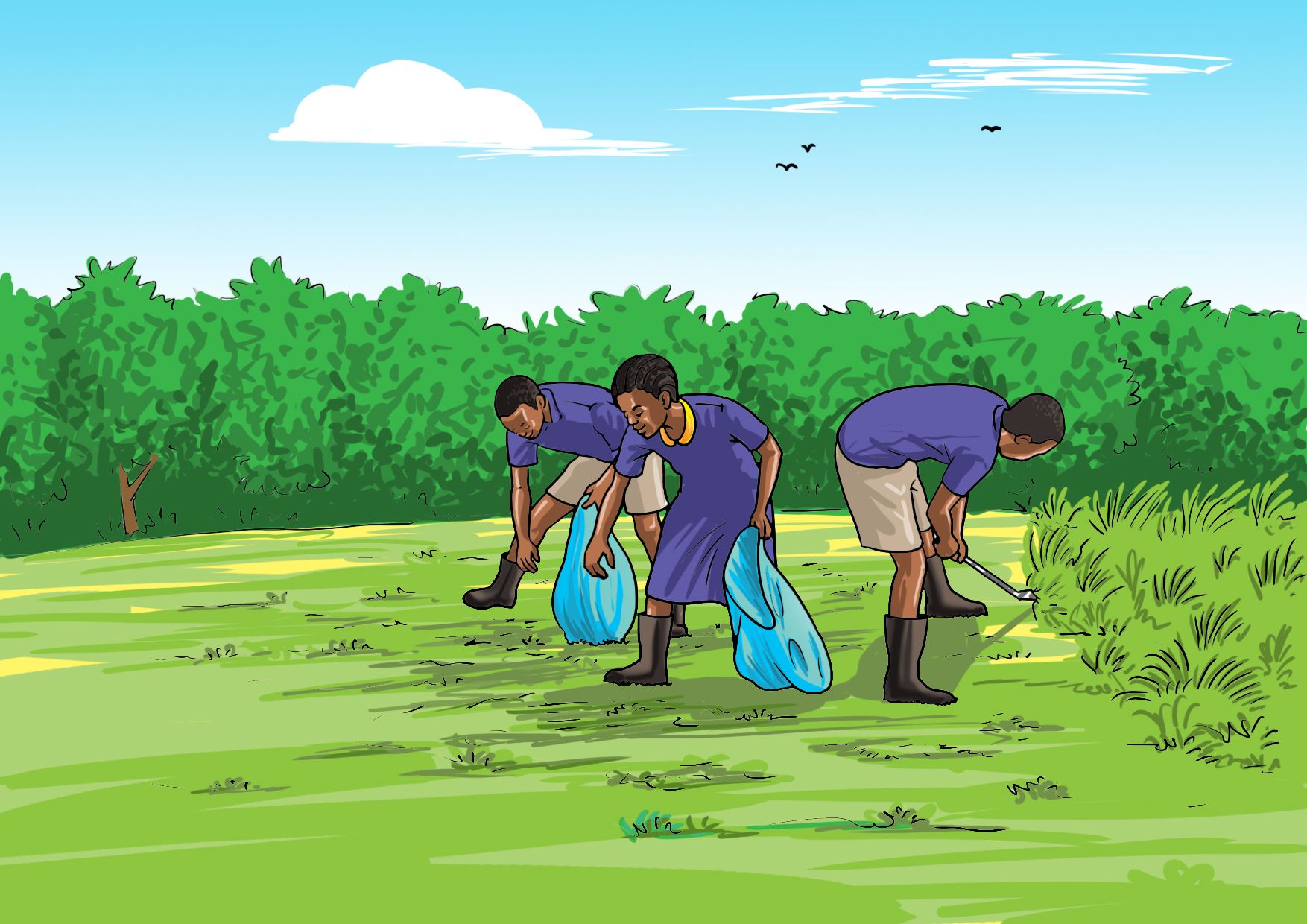
Care of the vegetable nursery bed
After planting vegetable seeds in the nursery bed, they should be taken care of. The caring practices include removing the mulch materials.
Activity 6
Taking care of the vegetable nursery bed.
Let us practice
- Visit the vegetable nursery bed.
- Find out whether the vegetable seeds have germinated.
Working in groups
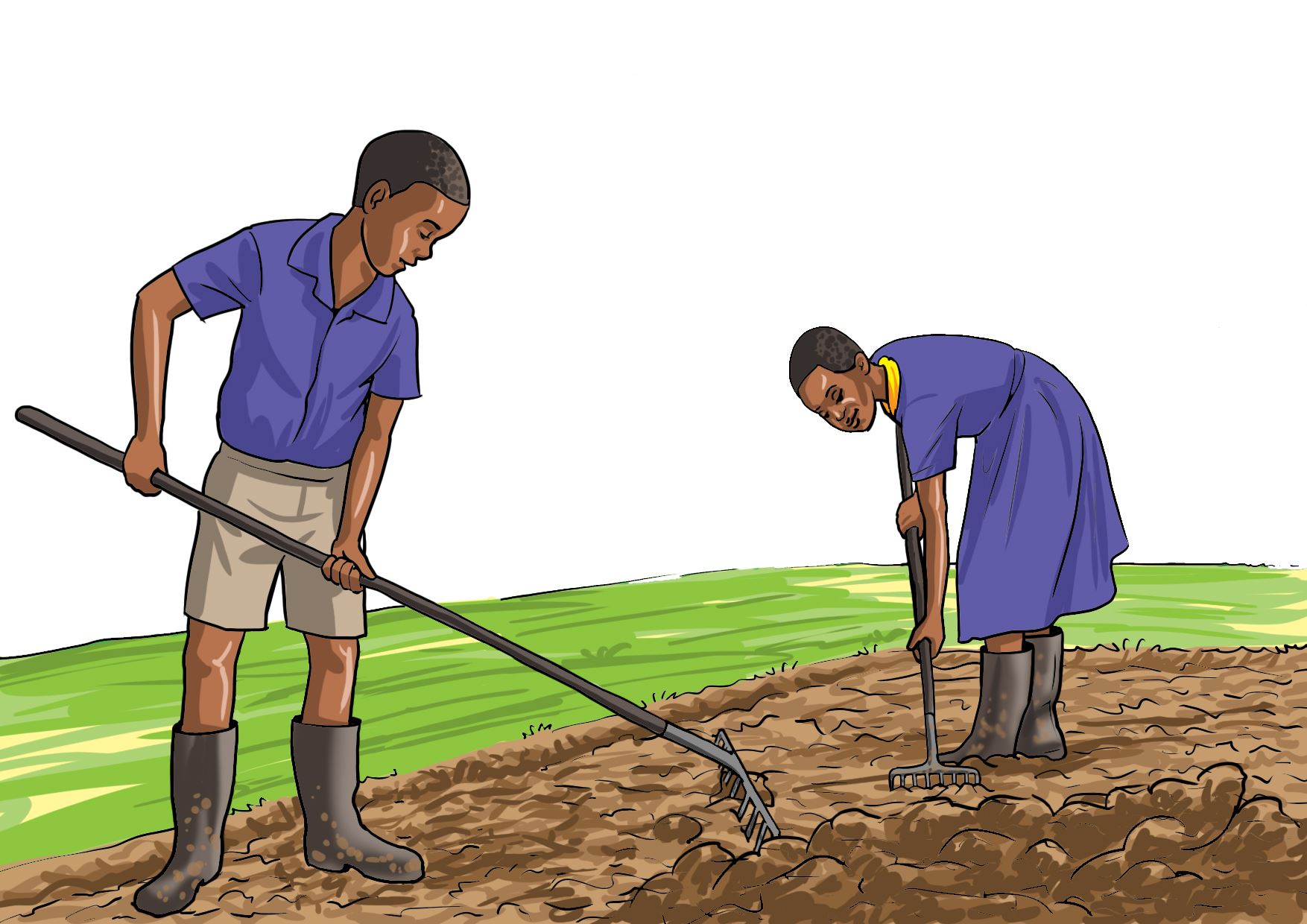
Carry out activities shown in the following pictures for your vegetable nursery bed.
A.
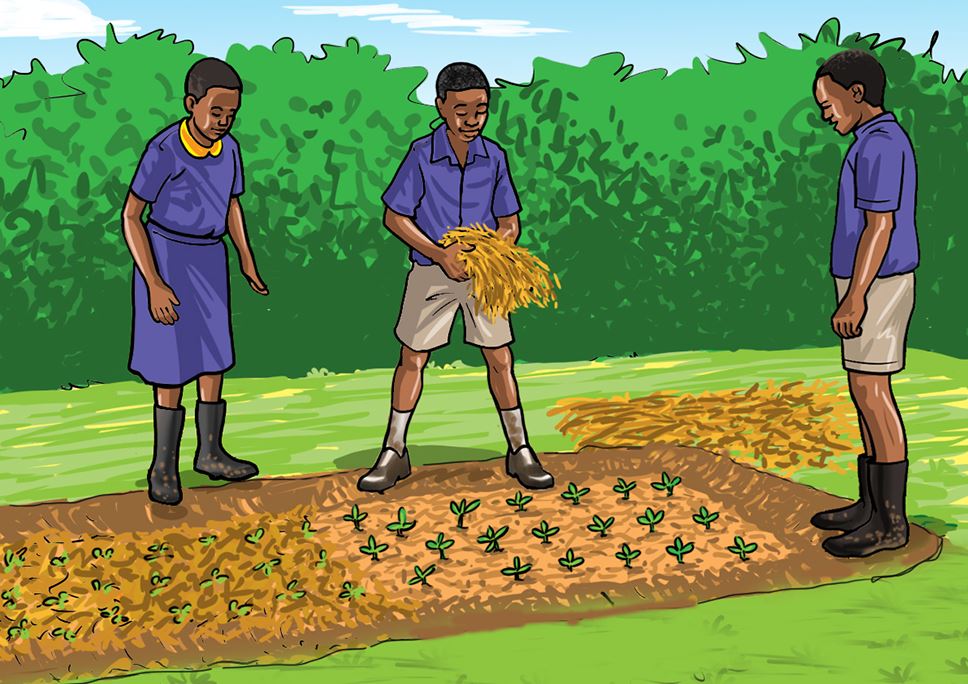

B.
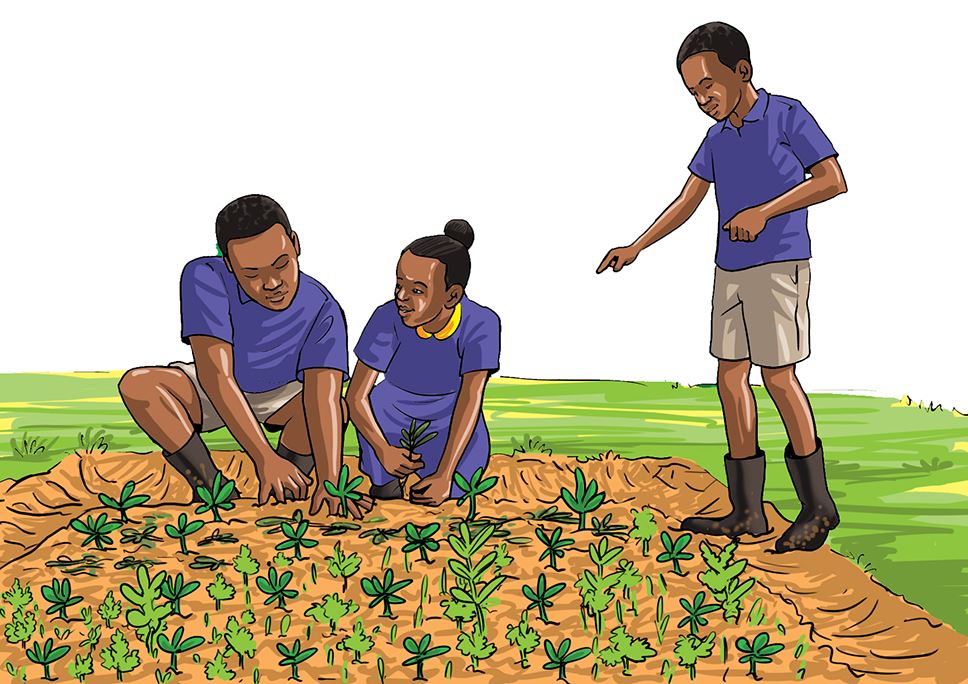

C.
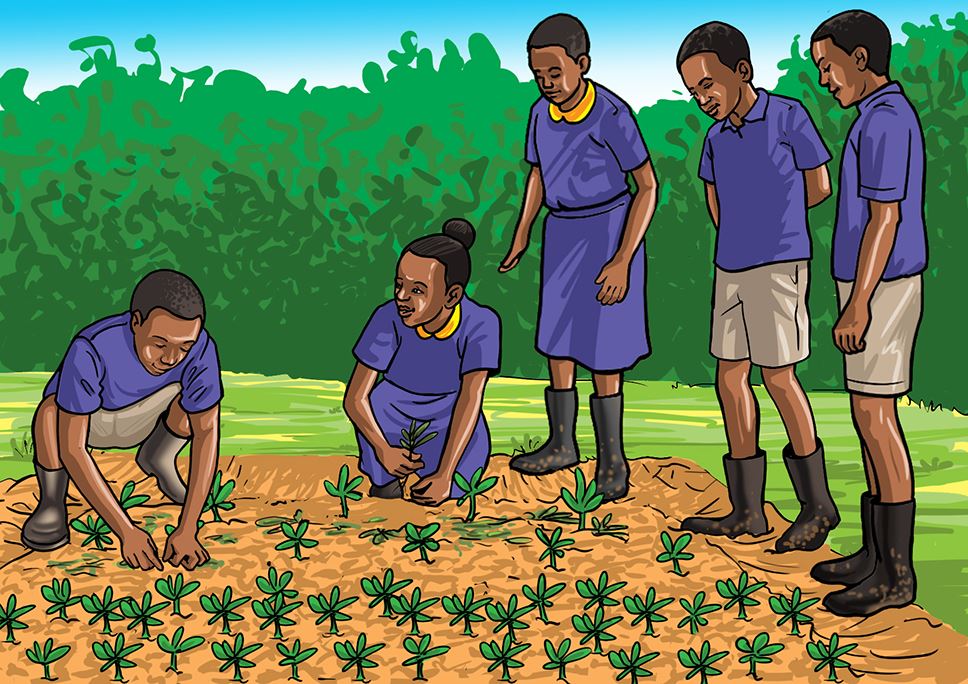

D.

Share your experiences with the other group.
Let us understand
- Removing the mulch material helps seedlings to grow straight and healthy.
- Uprooting weeds gives the seedlings enough space to grow.
- Thinning is done to avoid overcrowding of seedlings.
- Watering seedlings is done during dry periods.
- A shade is placed to conserve water.
Transplanting vegetable seedlings
When we take care of the vegetable seedlings in the nursery, they grow strong and healthy. They should be transplanted to the seedbed where they grow until harvesting.
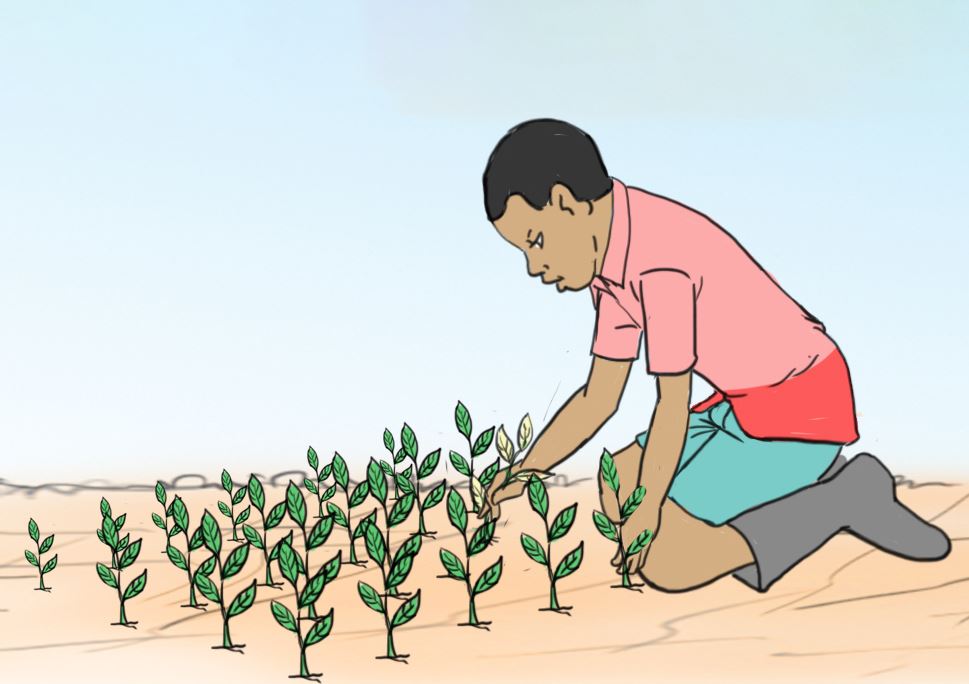
Working in groups
Activity 7
Transplanting vegetable seedlings into a prepared seedbed.
Let us practice
- Visit the nursery beds.
- Find out whether the vegetable seedlings are ready for transplant.
- Transplant the seedlings in the prepared seedbed using the steps shown in the pictures labelled a, b, and d.
A.

B.
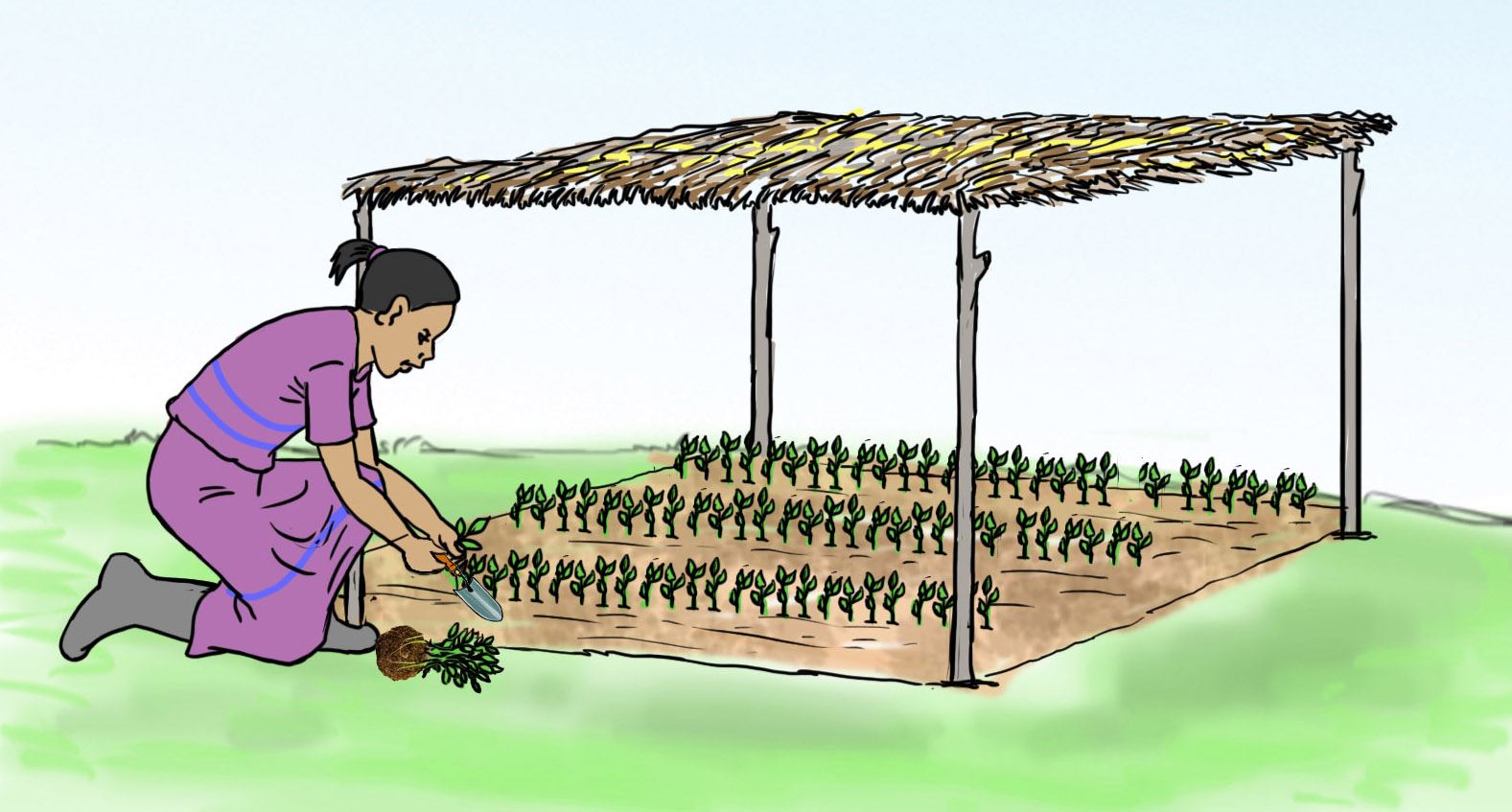

C.
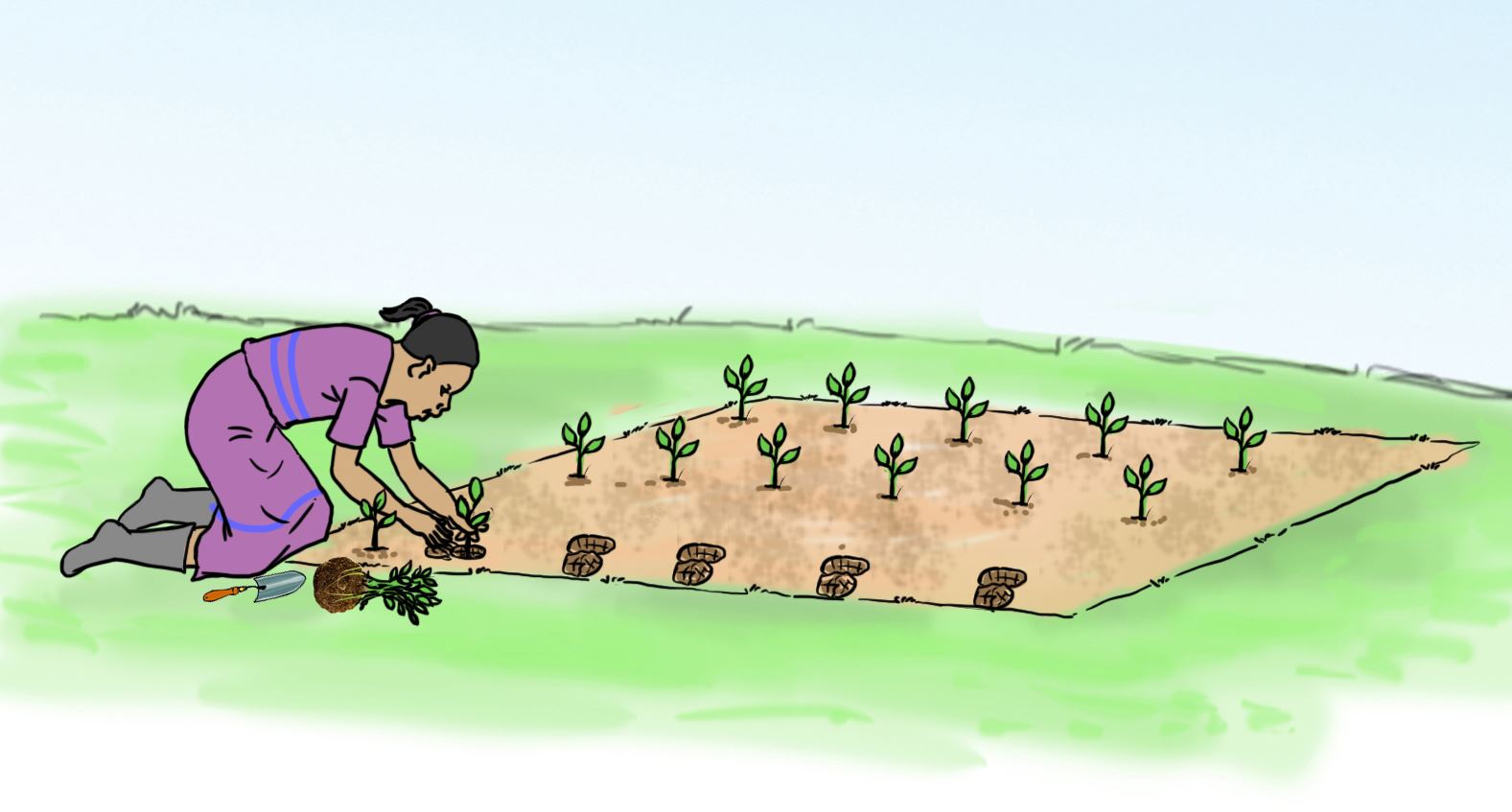

D.

Let us understand
- The nursery bed is watered to enable seedlings come out with roots during uprooting.
- Strong and healthy seedlings should be transplanted.
- A seedling is uprooted with a garden trowel to help it came out with all the roots.
- Mulch is applied after transplanting to conserve water.
- The seedlings are watered to avoid drying up.
Sale of vegetable seedlings
After transplanting, the remaining vegetable seedlings can be sold to the community to earn income.
Activity 8
Selling surplus vegetable seedlings to the community.
Working in groups
Organise with the teacher how to sell the remaining seedlings to the community.
Let us practice
- Suggest how you will prepare the seedlings for sale. Use the illustrations labelled a, b, c and d to guide your activity.
A.
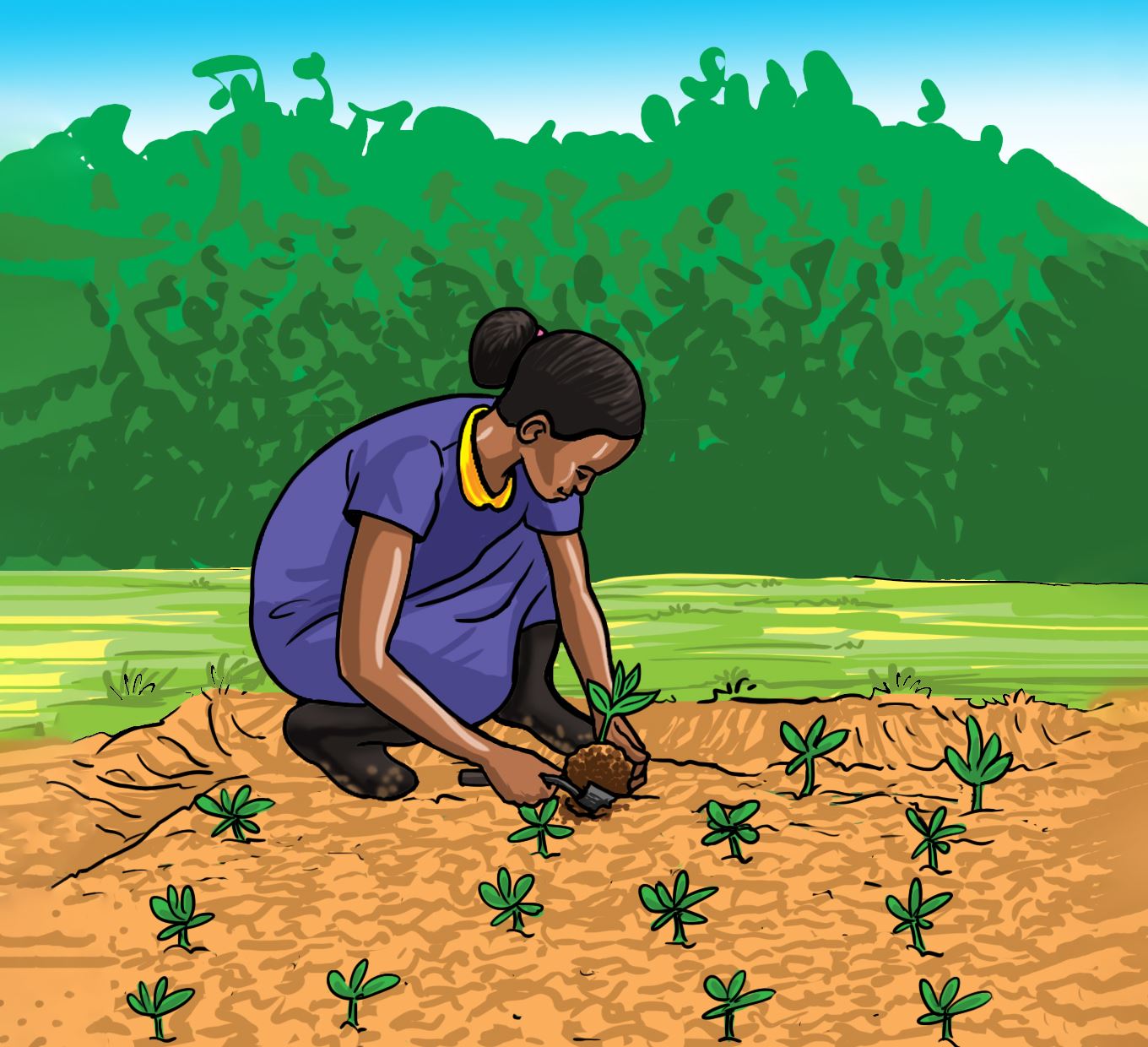

B.
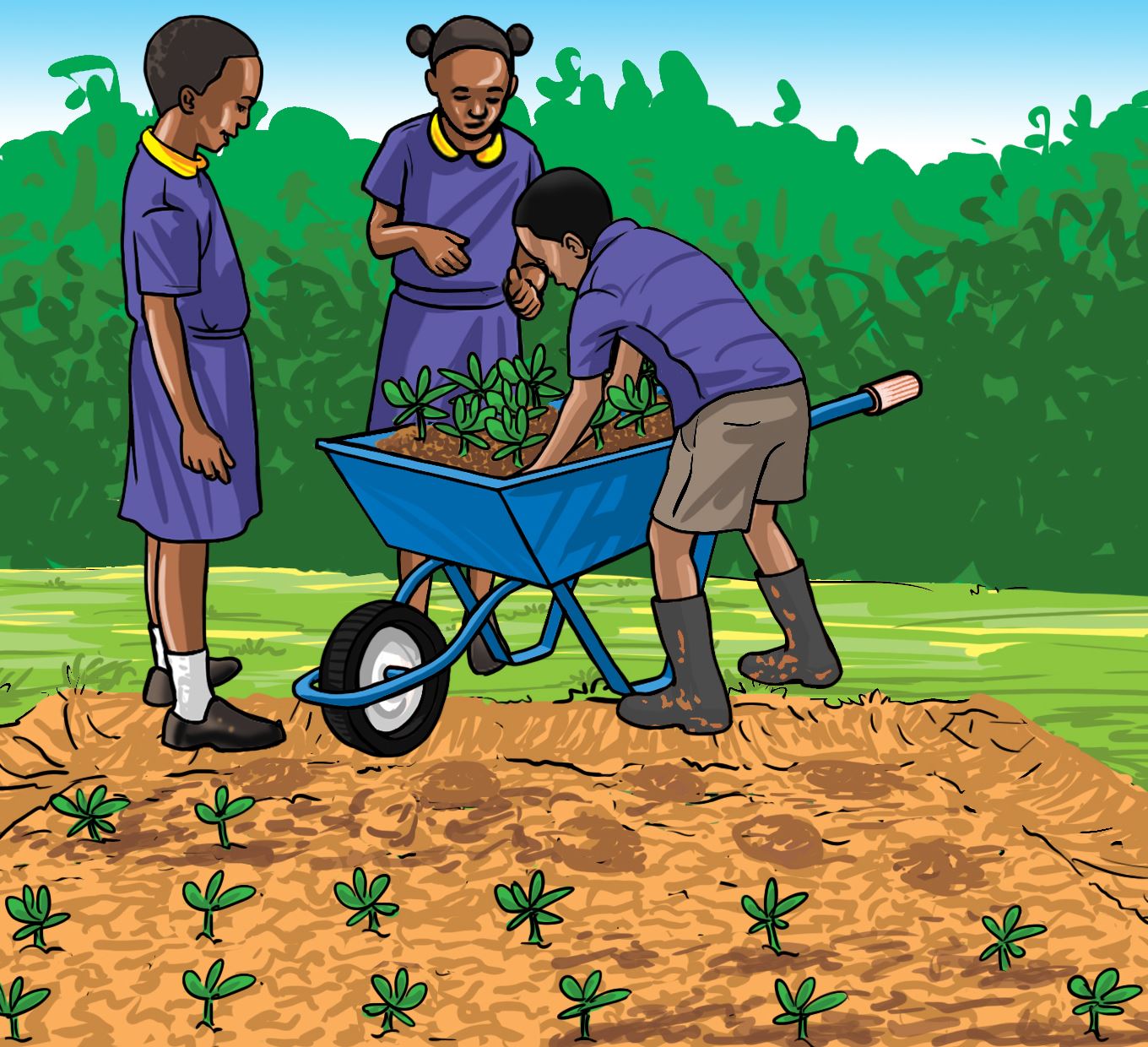

C.

D.

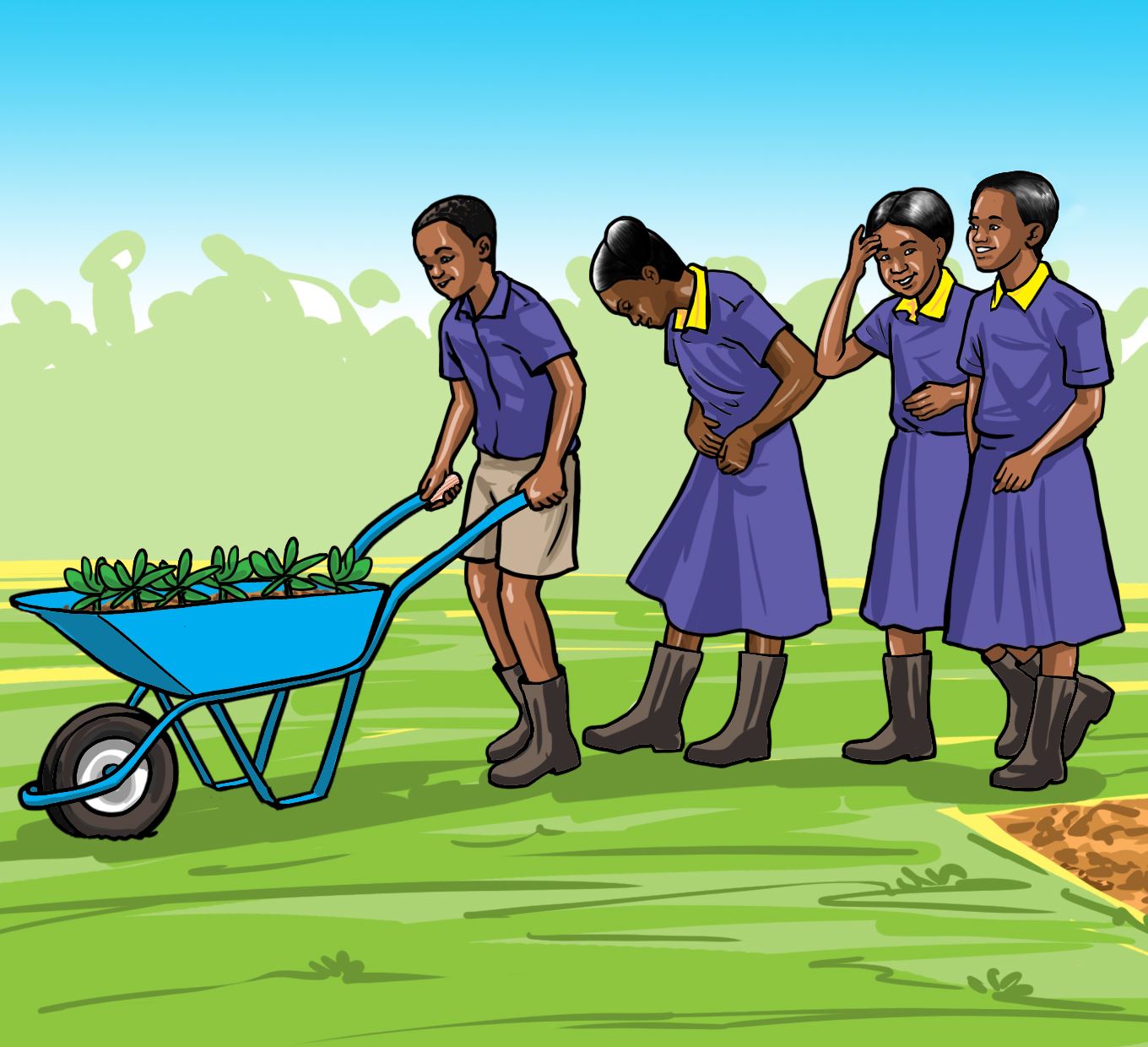
- Discuss how you will let the community and the member of staff know that there are seedlings for sale in the school.
- Sell the seedlings to the community around the school and the school staff.
- Discuss how you will use the money earned from the sale of vegetable seedlings.
Let us understand
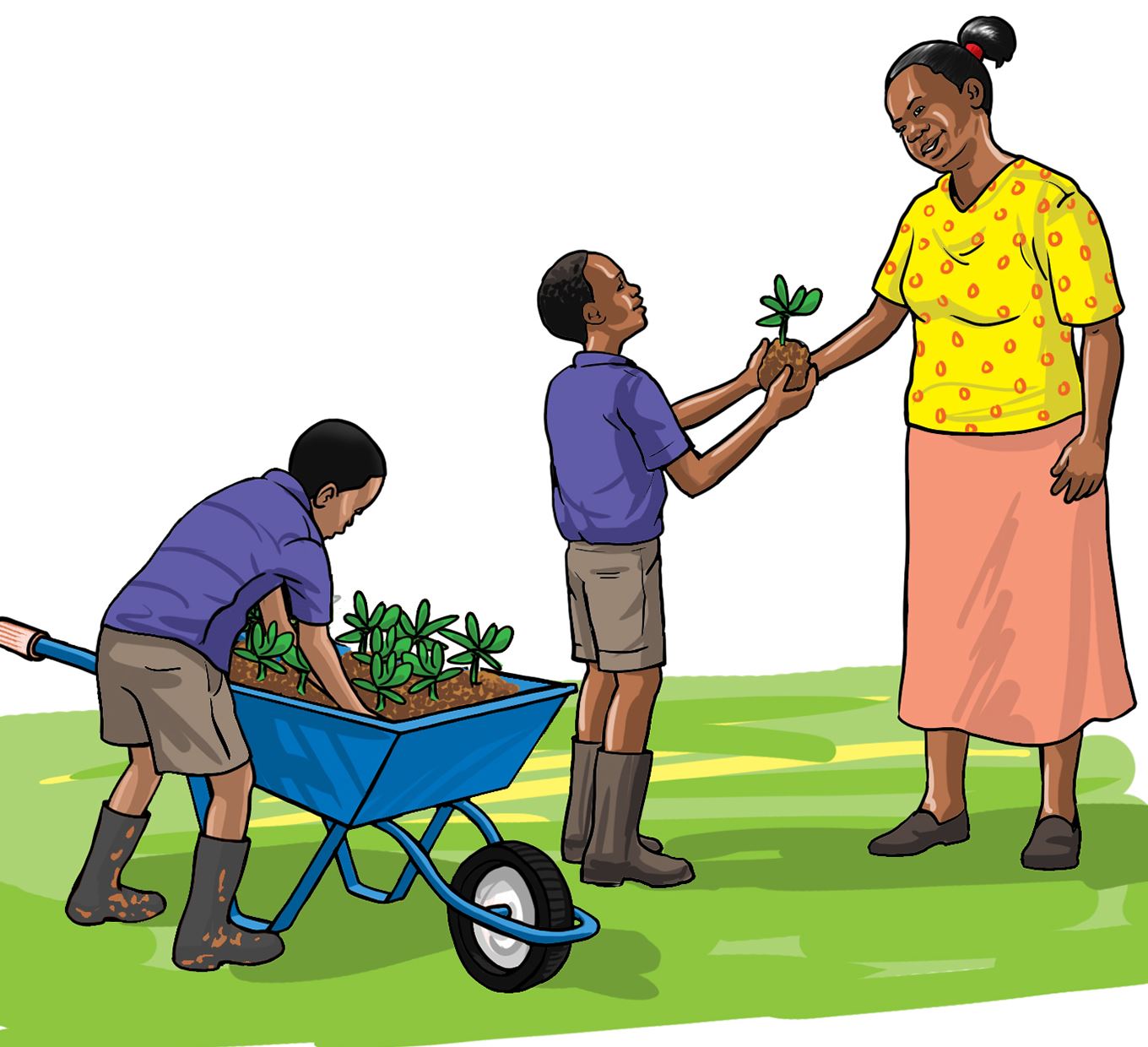
- Wrap the ball of soil around the roots to prevent drying.
- Only the strong and healthy seedlings should be sold.
- Leave the weak seedlings in the nursery bed to continue growing.
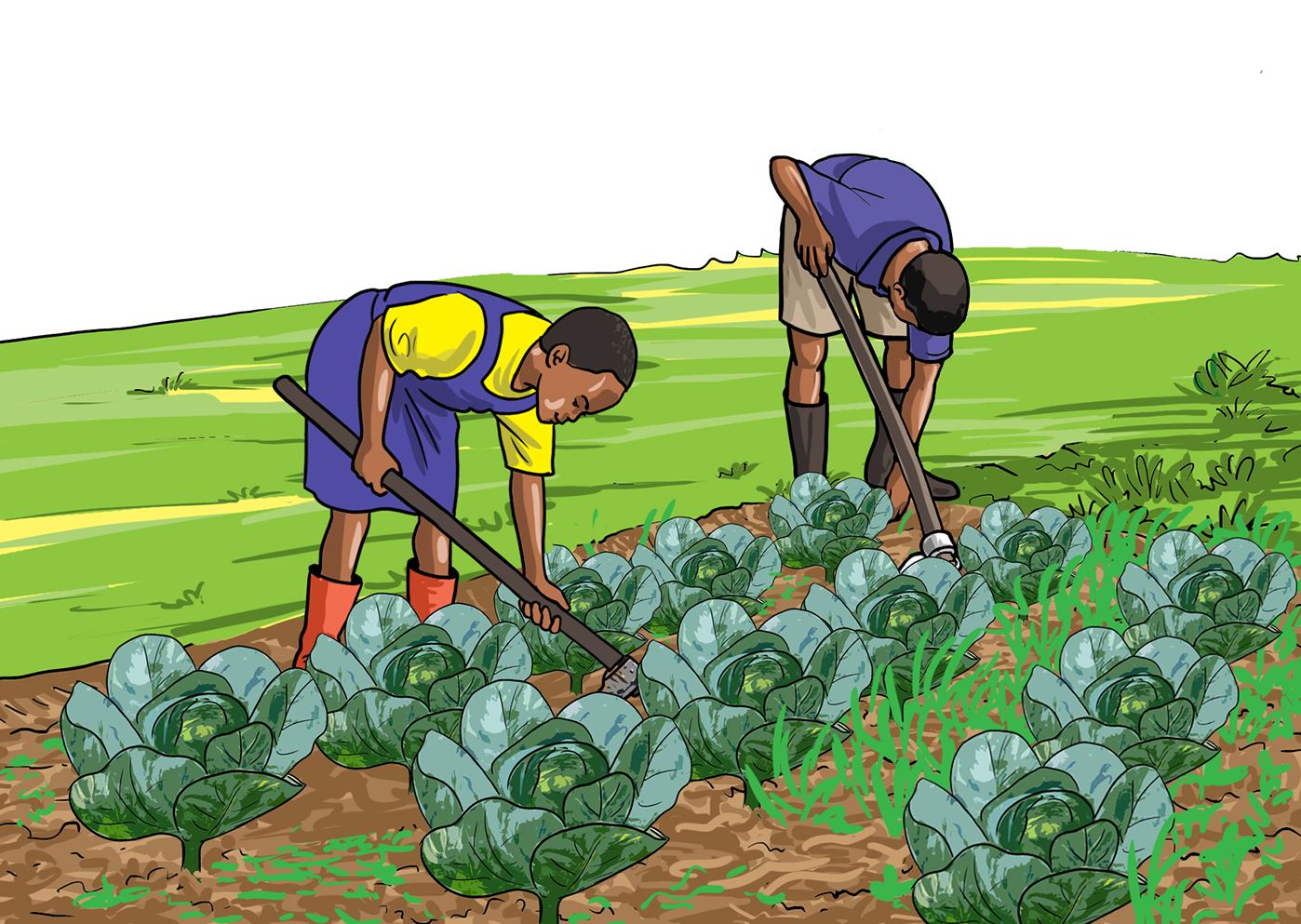
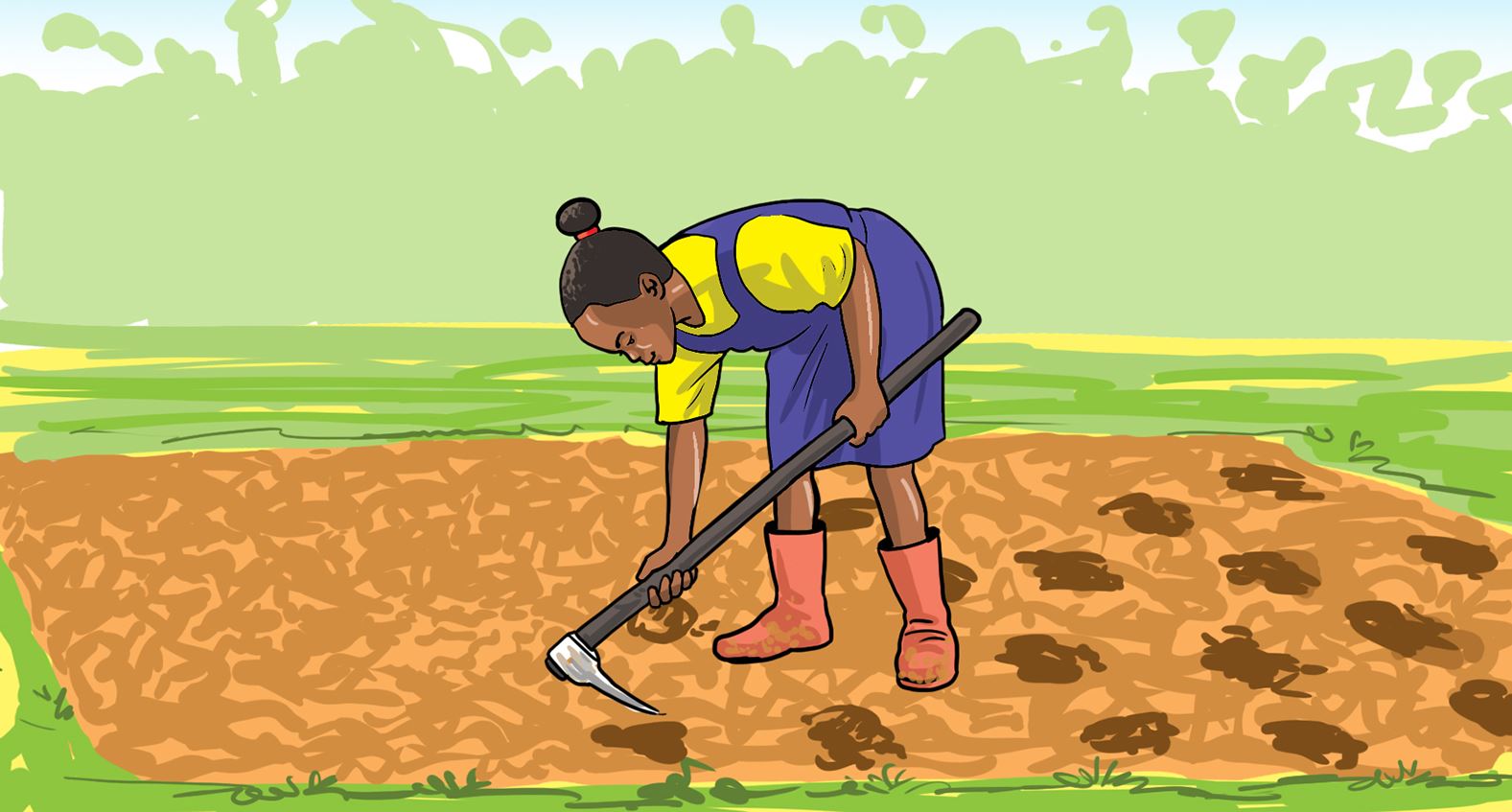
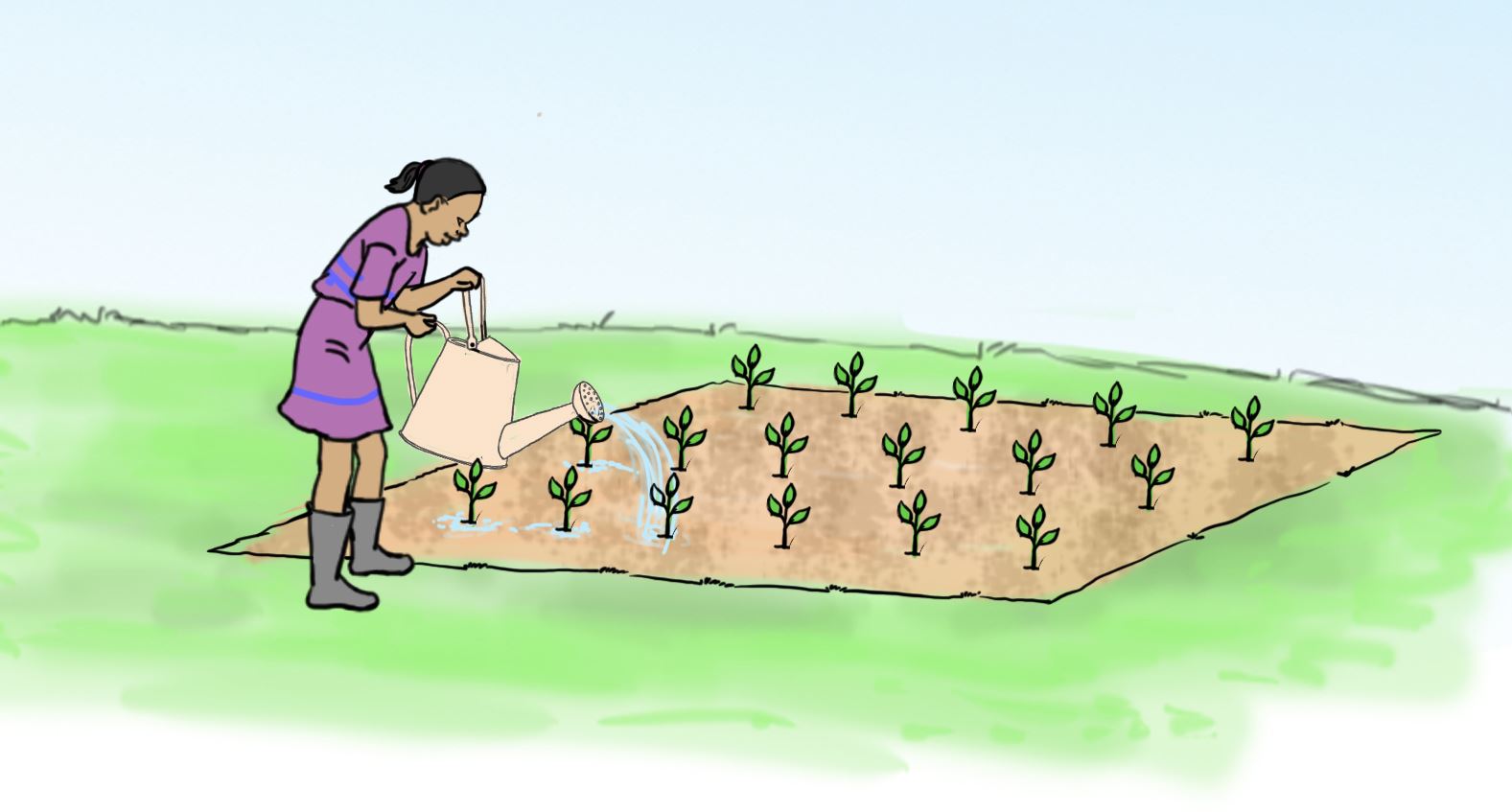
Care of established vegetable crops
Vegetables require some care to grow healthy after transplanting. The care for a vegetable crop in a seedbed include weeding, mulching, watering and removing diseased plants or plant parts.
Activity 9
Taking care of vegetable crop in a seedbed.
Let us practice
- Discuss how to take care of the vegetable crops.
- Name the tools you will use for each activity.
- In the vegetable garden, carry out the activities shown in pictures a, b, c and d.
- Use tools and equipment correctly for your own safety and that of others.
A.
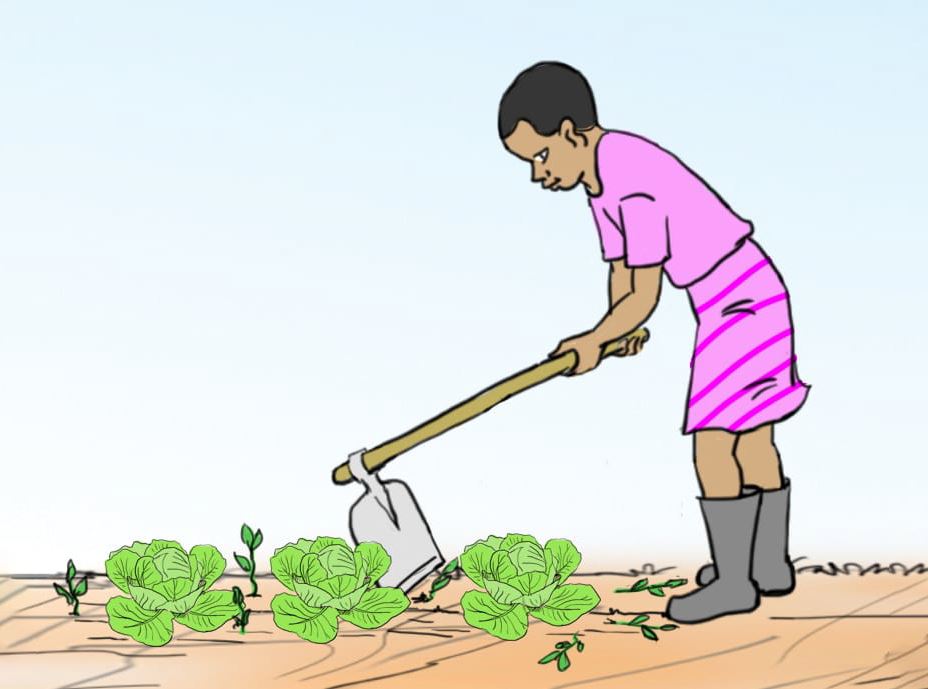

B.
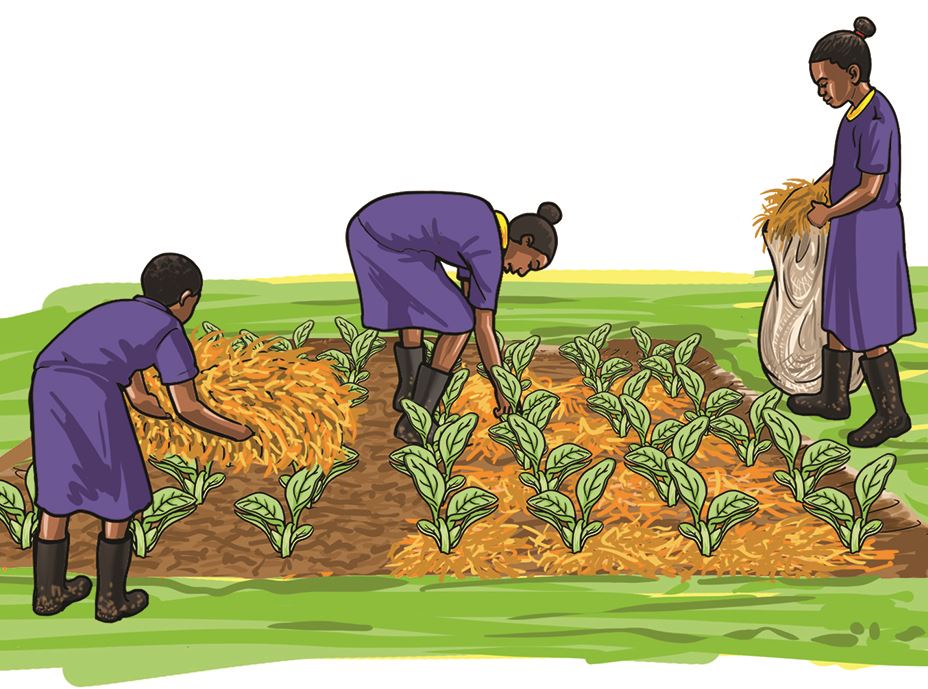

C.
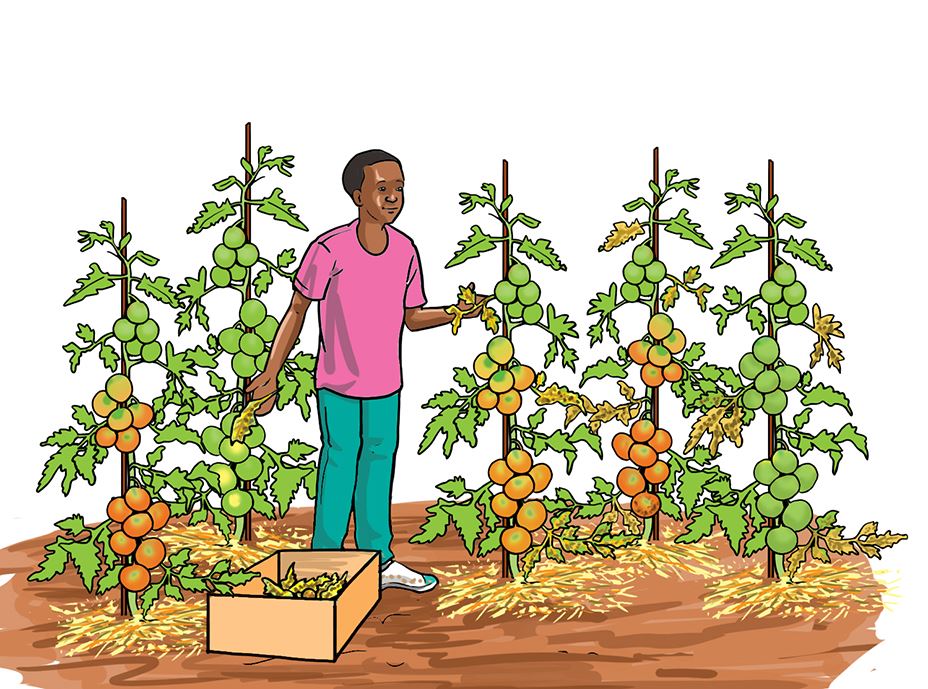

D.
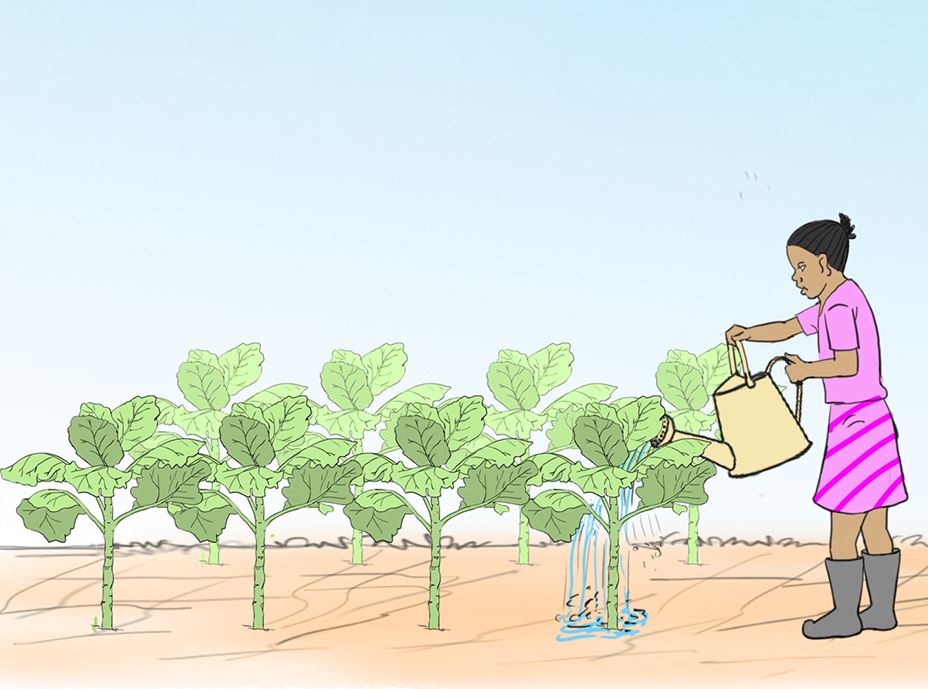

Let us understand
- When we take care of vegetables, they grow healthy and strong.
- Using tools and equipment correctly prevents damaging the vegetable crop and prevents accidents.
- Tools and equipment which are used correctly last longer.
Choice of tools and equipment for taking care of vegetable crops
Activity 10
Using appropriate tools and equipment to take care of vegetable crops.
Let us practice
Working in groups
- Discuss the tools and equipment that you need to take care of vegetable crops.
- The following pictures show the correct use of some tools and equipment.
Identify the tools and equipment in use.
A.
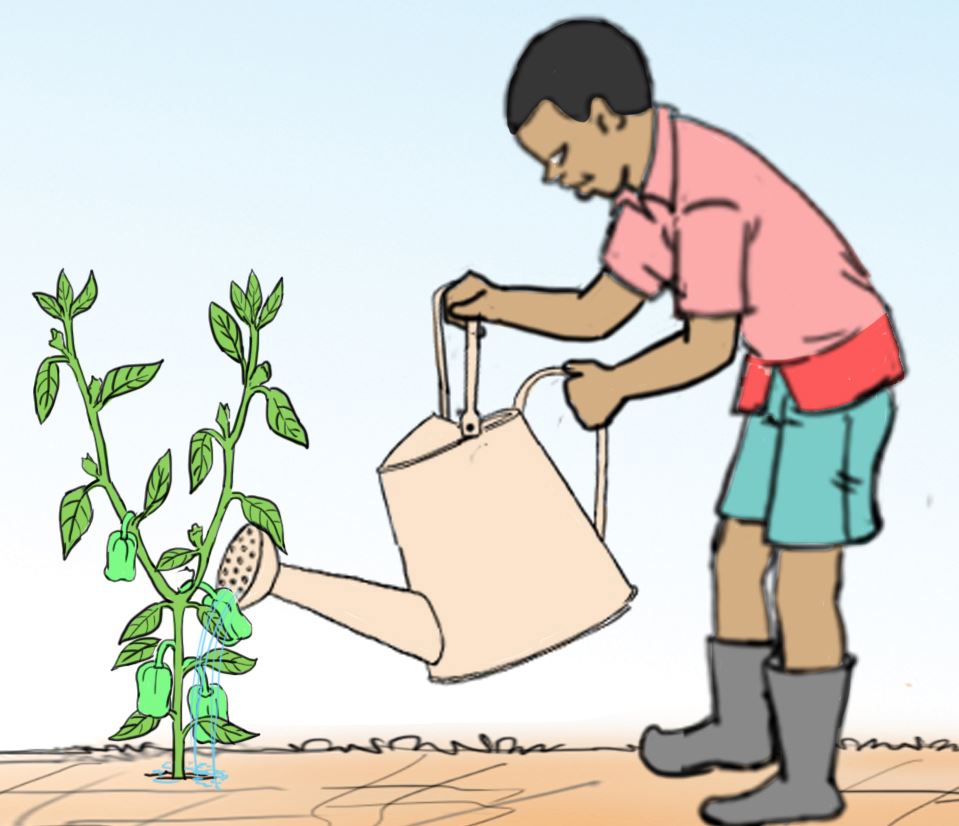

B.
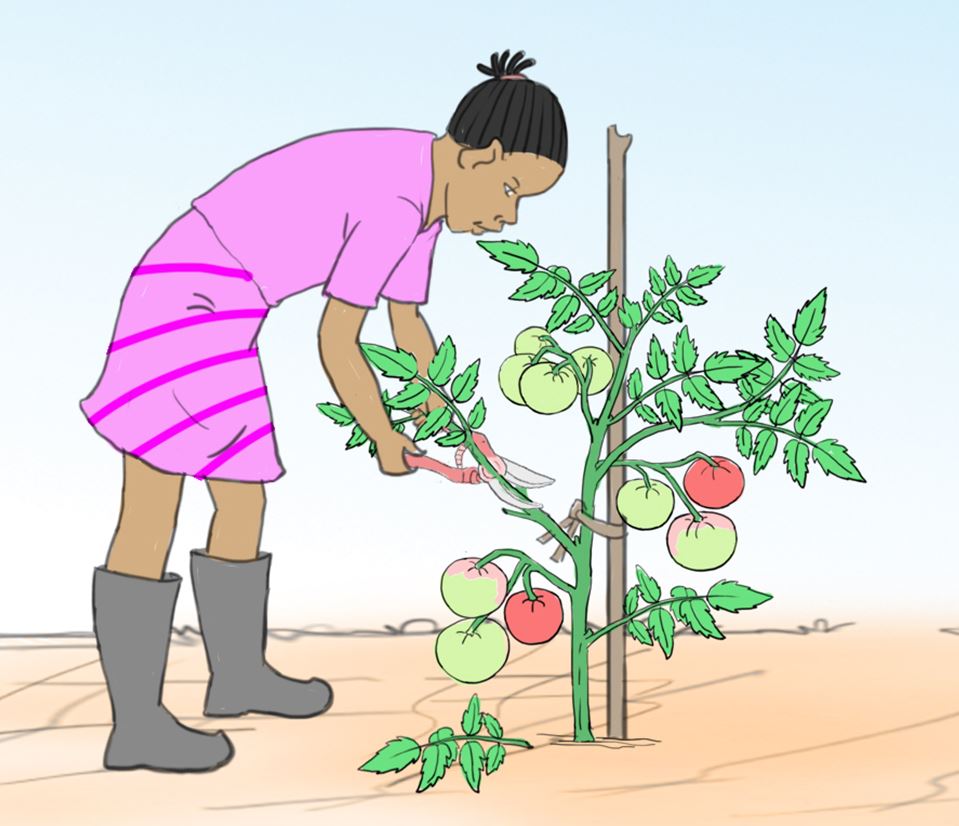

C.
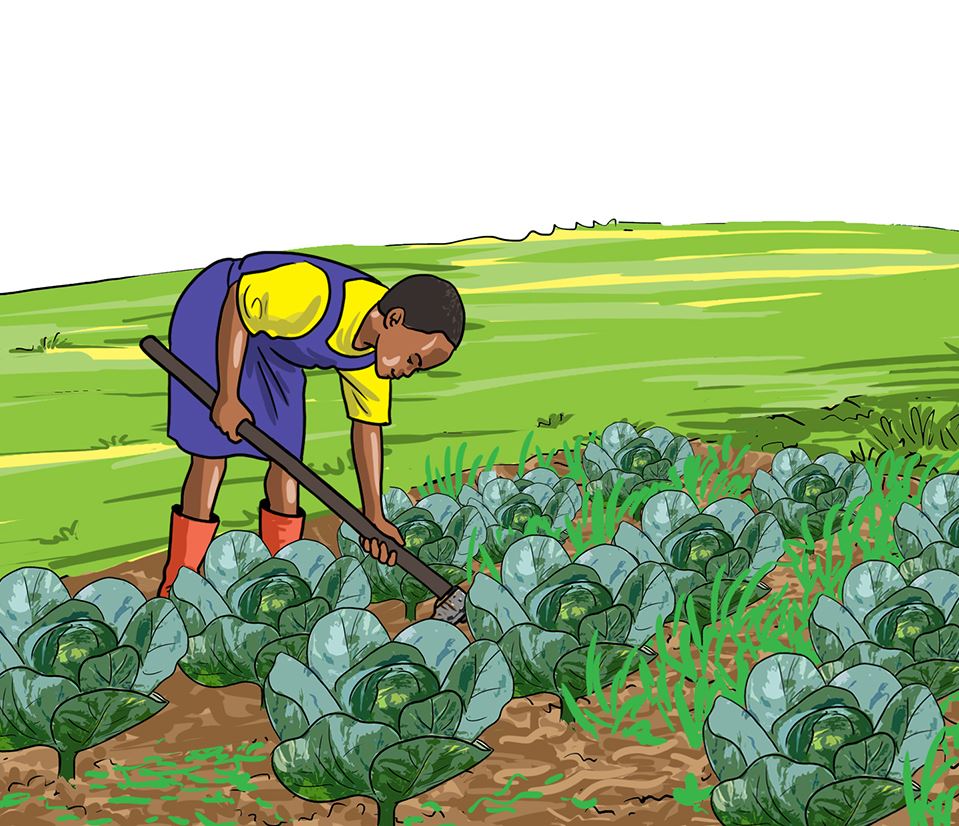

- Are the tools and equipment being used correctly?
Share your findings with the other groups.
Other tools and equipment used to taken care of vegetable crops are shown in the following pictures:
(i)
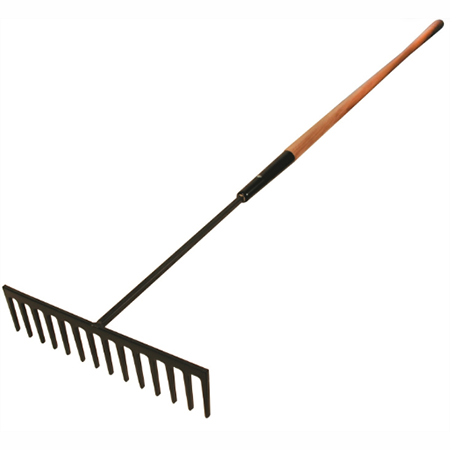

(ii)
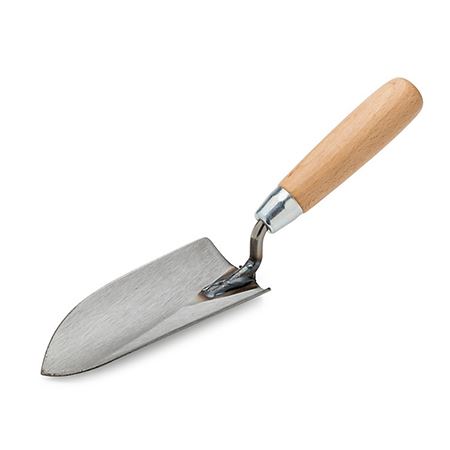

(iii)
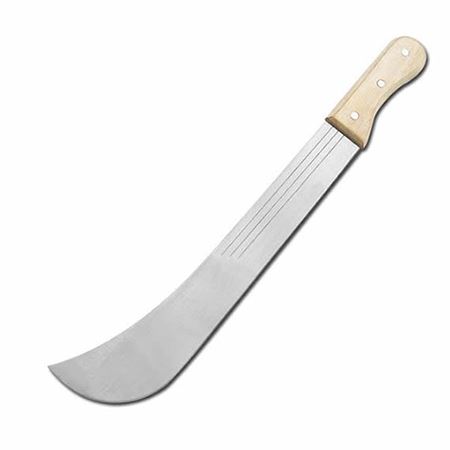

(iv)
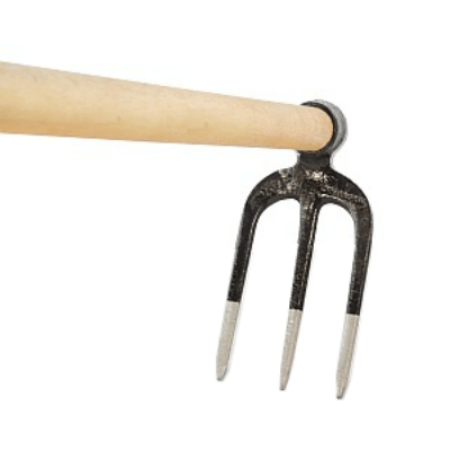

(v)
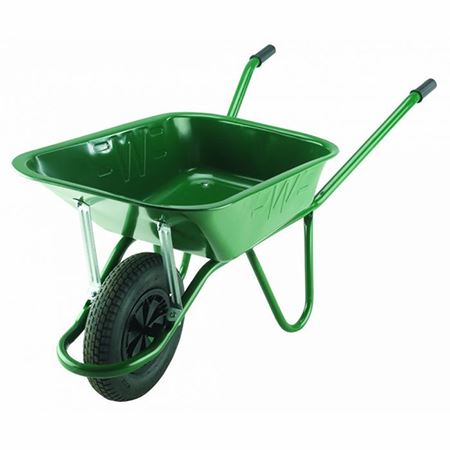

(vi)
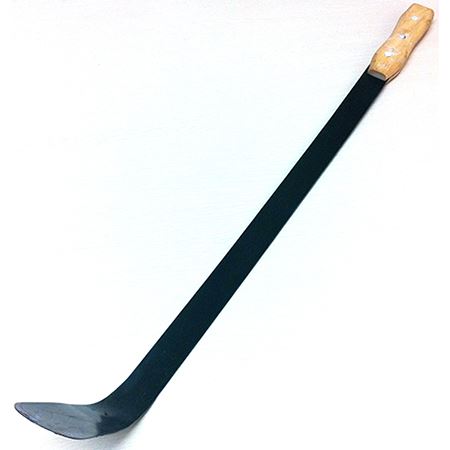

- Select each tool name from the select bar.
- Name the correct use of each tool in the pictures (i) to (vi).
Let us understand
- Tools and equipment used when taking care of vegetables should be selected correctly.
- Use the correct tools for the correct purpose.
- Tools and equipment should be handled carefully when in use to avoid injury to yourself and to others.
- Tools or equipment that are not correctly used get damaged easily.
Maintaining tools and equipment
Activity 11
Home project
Assisting parents or guardians in maintaining tools and equipment at home.
The tools and equipment that we use at home in growing vegetables need to be well maintained.
Let us practice at home
- Tell your parents or guardians why gardening tools need to be maintained.
- Help your parents or guardians to maintain gardening tools and equipment at home.
- Ask your parents or guardians to tell you other ways of maintaining the tools and equipment.
Let us understand
- Gardening tools and equipment should be maintained in order to last long.
- Properly maintained tools and equipment are easy to use.
- It is safe to use well maintained tools and equipment.
- Ways of maintaining tools and equipment include:
- Sharpening
- Tightening screws
- Greasing moving parts
- Repairing broken parts
- Fixing handles
- Applying oil to prevent rusts
- Cleaning
1. We grow vegetables because:
- We need to eat vegetables everyday.
- They don’t need a lot of water.
2. Watering vegetables is done when:
- The vegetables are growing.
- The vegetables are being harvested.
3. A vegetable nursery should be with:
- Fine and sloppy soil.
- Fine and level soil.
4. Mulch is removed from around the seedlings to:
- Allow the seedlings to grow straight and healthy.
- Allow water to enter the soil.
5. When transplanting vegetable seedlings, we should avoid:
- Dropping the seedlings.
- Cutting the roots.
Stage at which vegetable crops are harvested
Activity 12
Discussing appropriate stage of harvesting vegetable crops.
Vegetable crops are harvested when they reach maturity.
Let us Find Out
Working in groups
Discuss with your group members how to find out whether the following vegetables have reached maturity:
- Cabbage
- Tomatoes
- Kales
- Spinach
Share your findings with the other groups.
Look at the following photographs and identify the vegetables that are ready for harvesting:
- A.
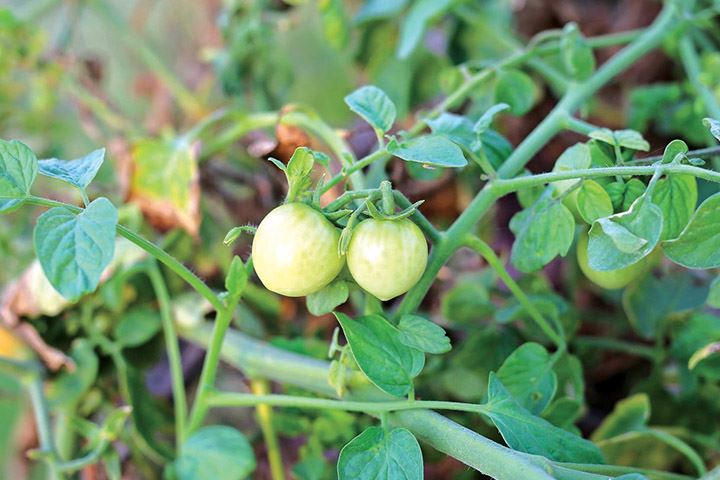

- B.
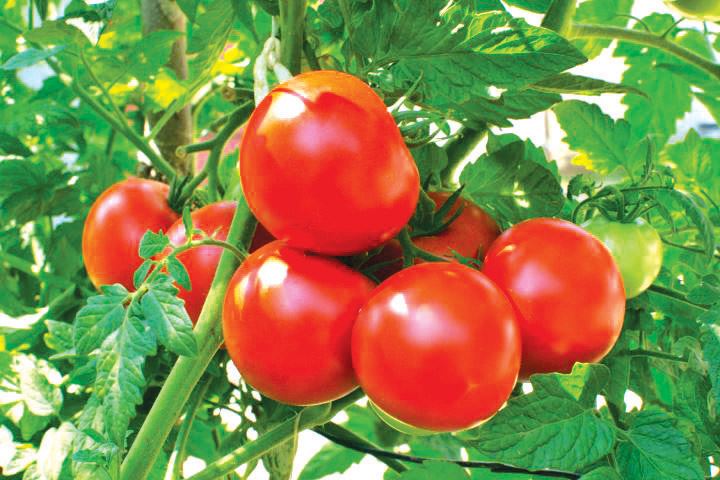

- C.
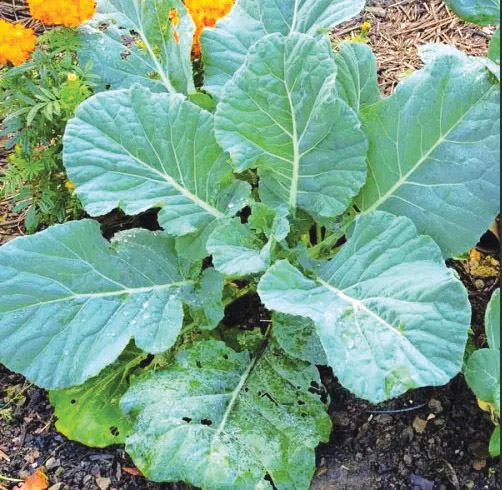

- D.
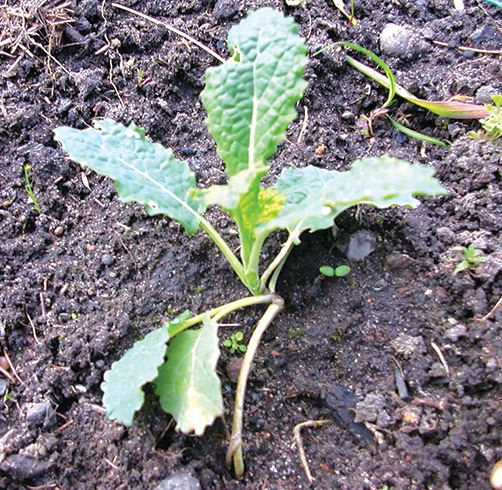

- E.
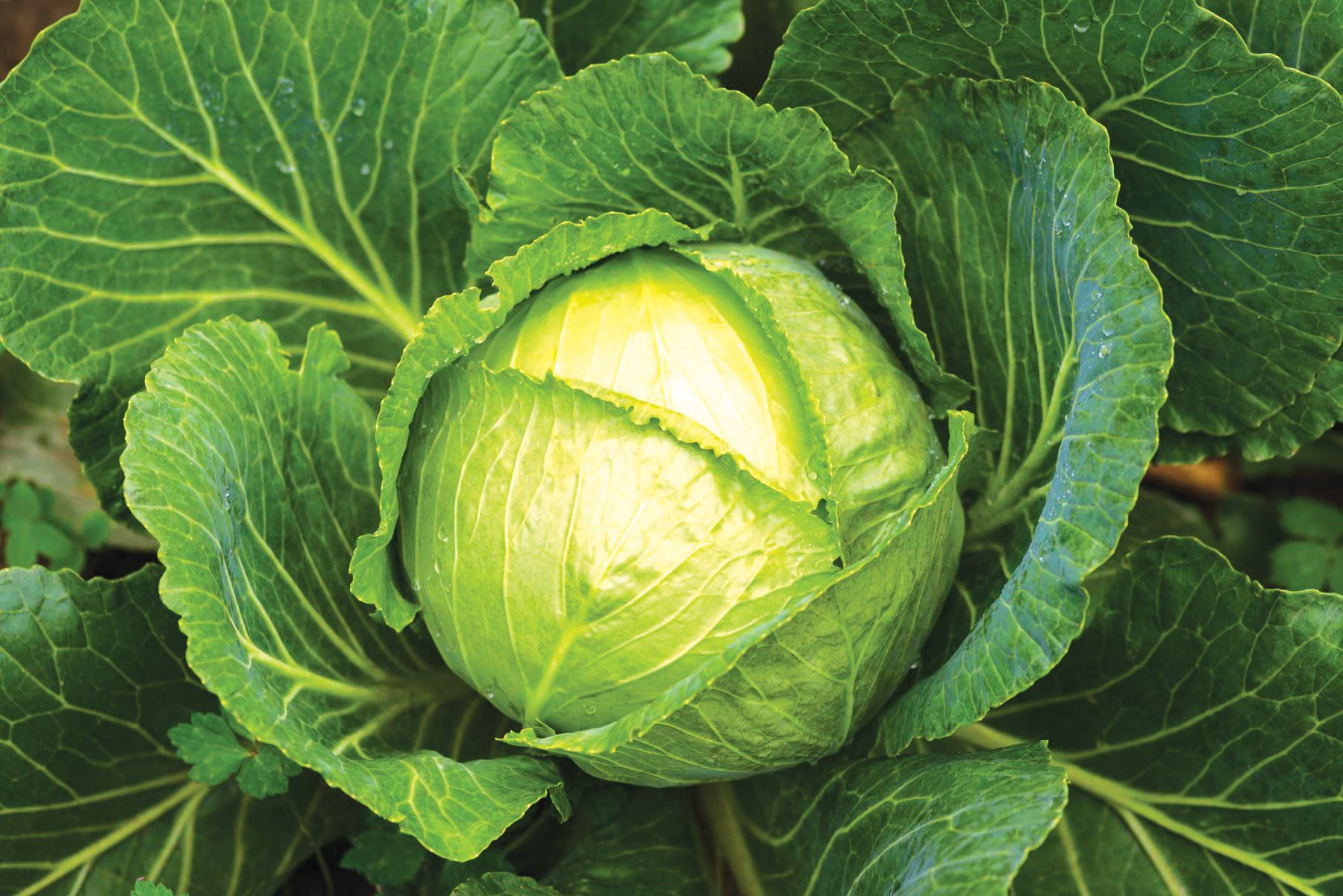

- F.
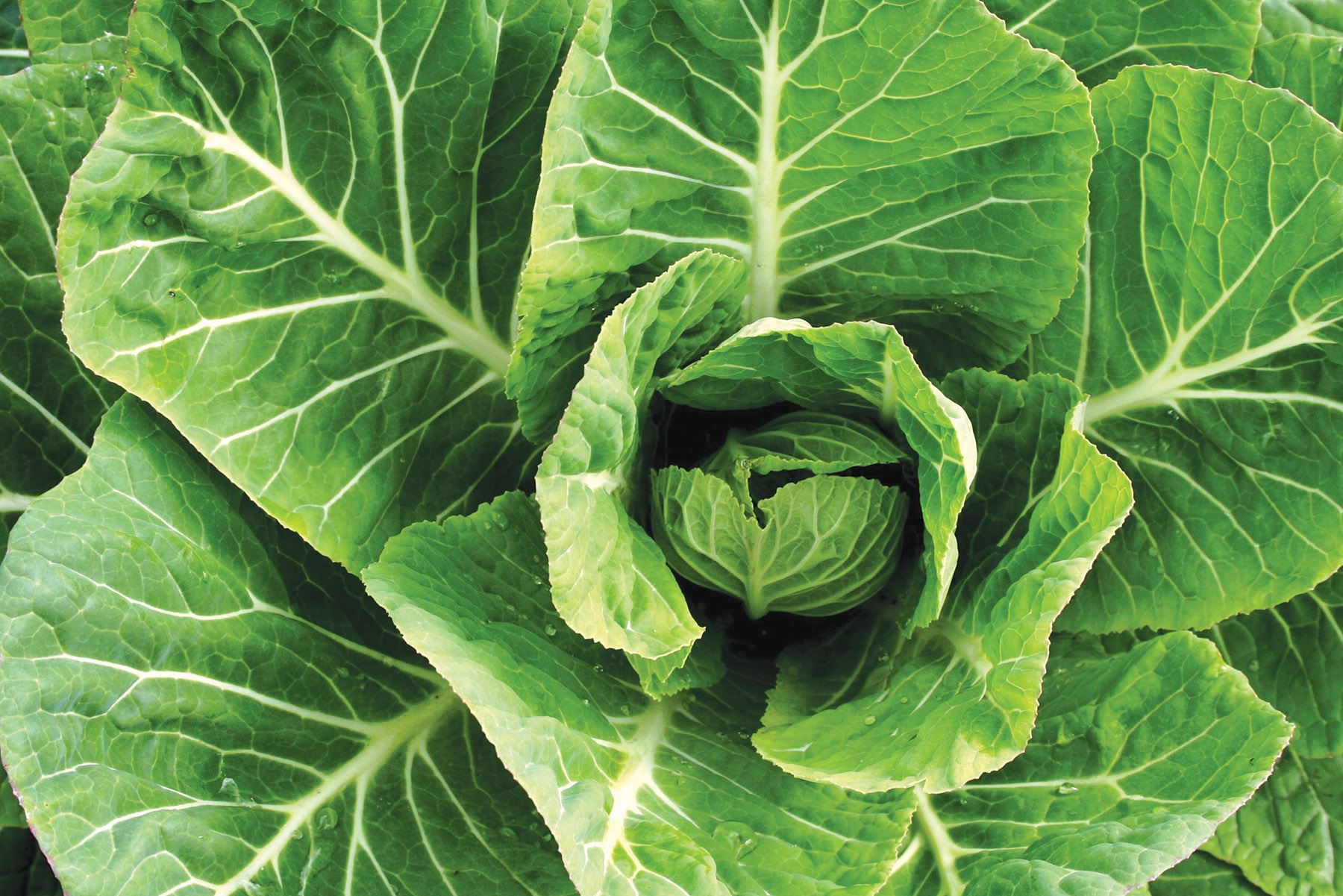

Let us understand
- Maturity determines the stage of harvesting vegetables.
- Maturity in vegetables can be determined by:
- Ripening or change in colour. This is observed in tomatoes.
- Increase in size.This is observed in crops like spinach.
- Drying of leaves.This is observed in crops like onions.
- Heads becoming firm.This is observed in crops like cabbages.
How to harvest vegetable crops
Vegetable crops are harvested by removing the edible parts from the plant.
Activity 13
Harvesting vegetables for consumption and nutrition.
Let us practice
- Look at the following pictures. Discuss in your groups the harvesting activity shown in the pictures a, b and c.
A.
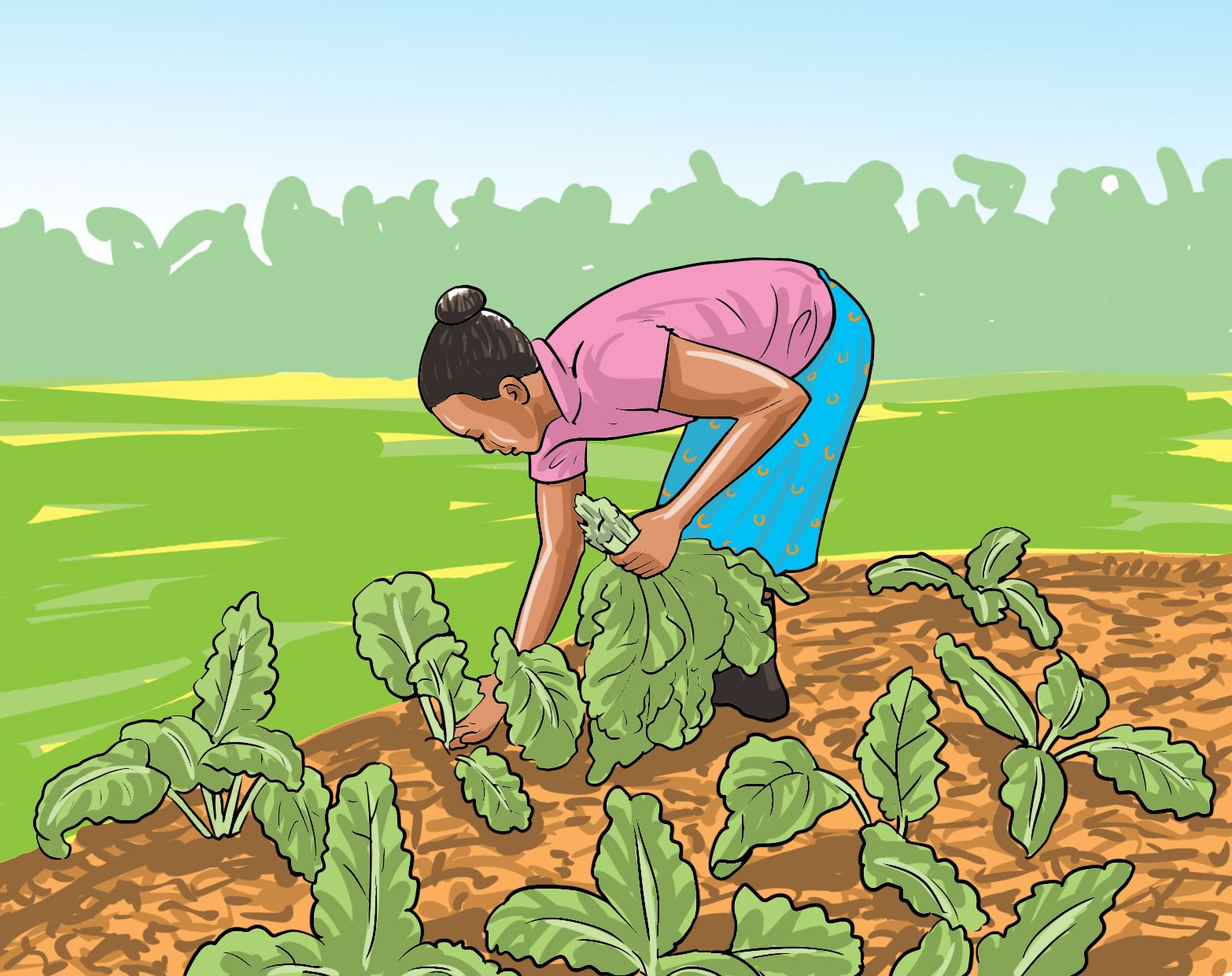

B.
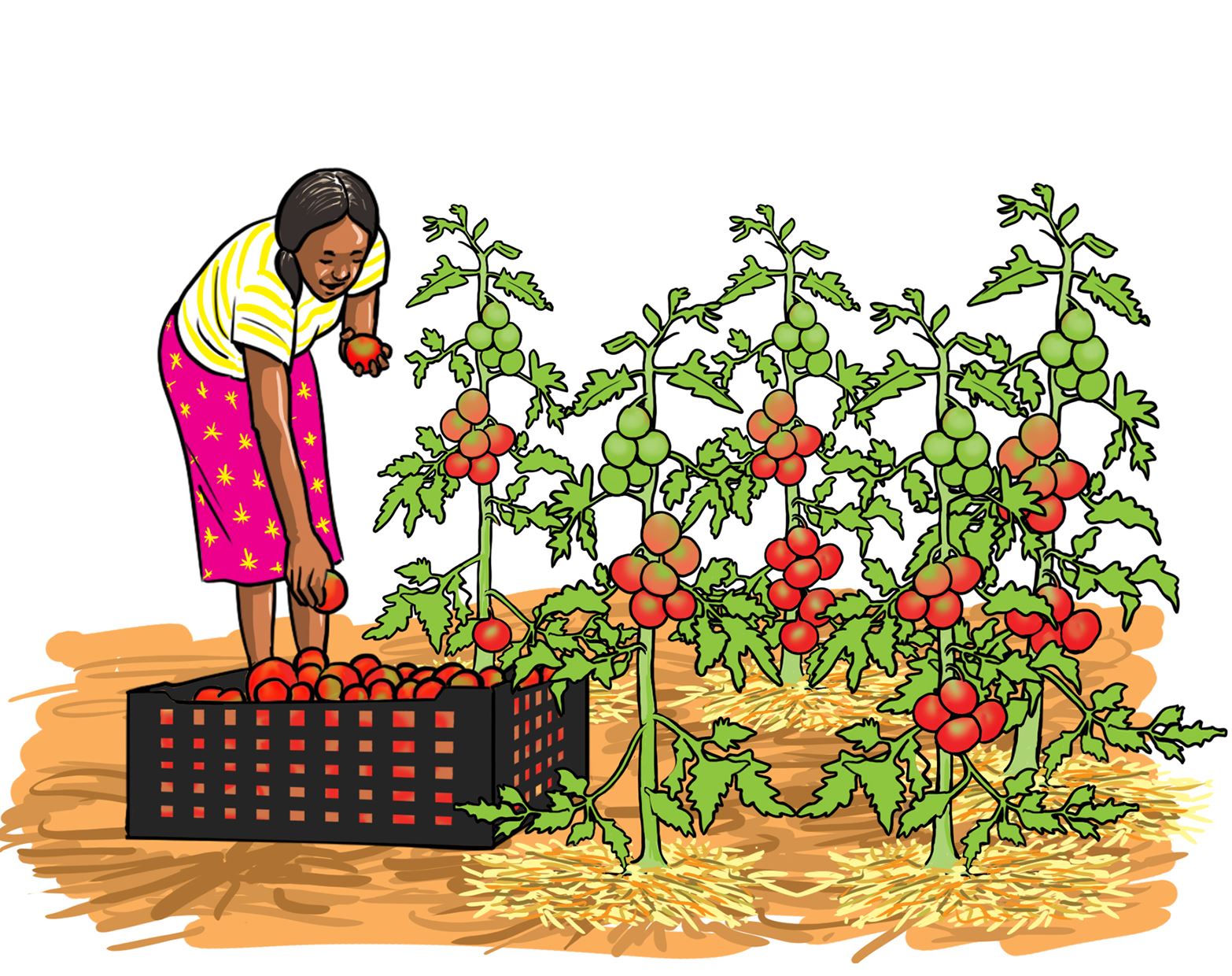

C.
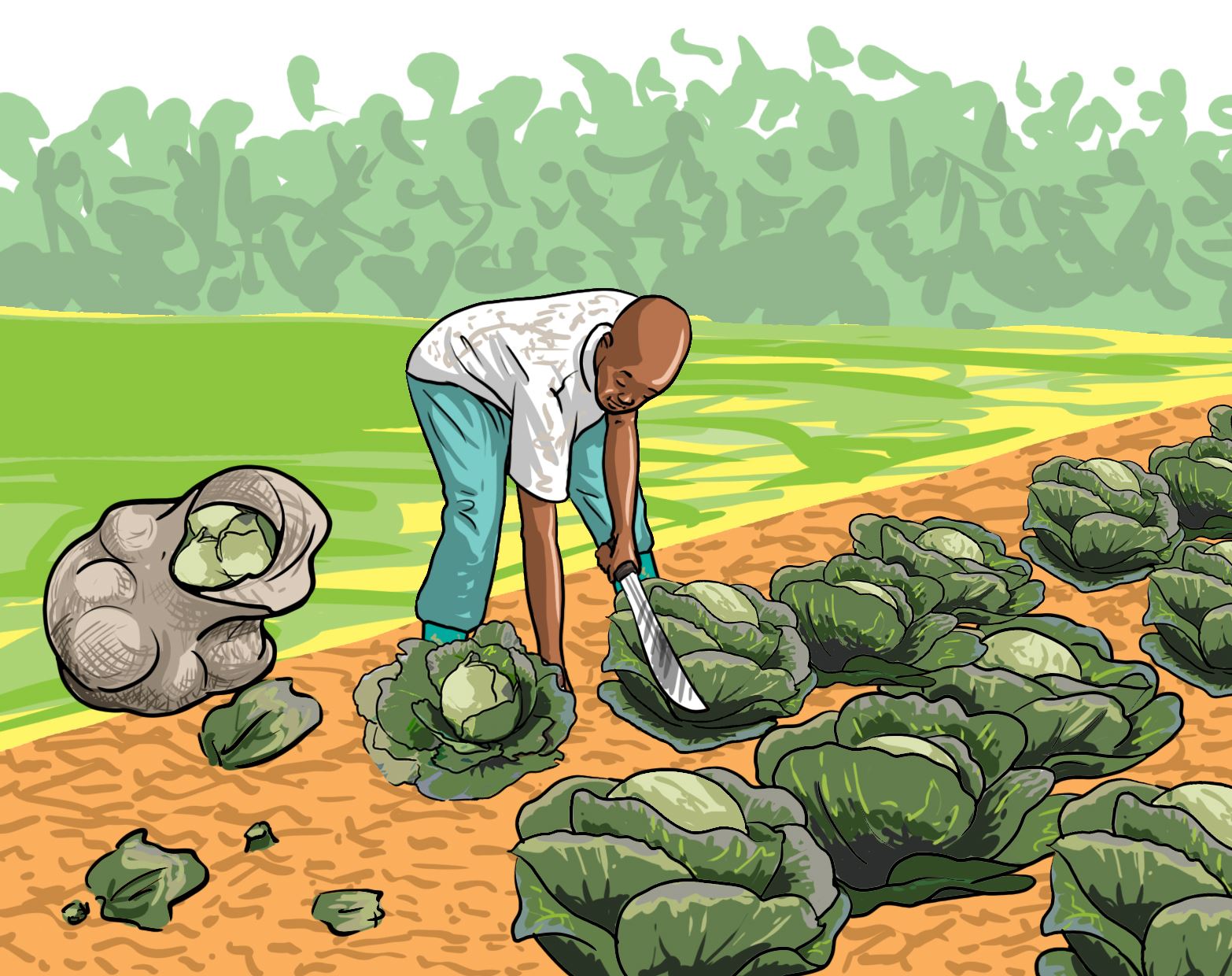

- Visit the vegetable garden. Check whether the vegetables are mature for harvesting.
- Harvest the mature spinach leaves by plucking them from the plant.
- Harvest ripe tomatoes by breaking the fruit stalk from the plant.
- Handle the harvested vegetables appropriately to avoid damage.
- Share your experiences with the other groups.
- Find out why we need vegetables in our diet.
Let us understand
- Damaged vegetables get rotten quickly. This leads to losses.
- Some vegetables are eaten immediately after harvesting to avoid rotting.
- Other vegetables can be stored for future use.
- Vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals. They therefore protect our bodies from diseases.
1. Vegetables are harvested when;
- They are mature.
- They dry up.
2. We sell surplus vegetables when;
- It is raining.
- We want to earn money.
3. We use when harvesting tomatoes.
Sale of surplus vegetables
Vegetables can be sold to earn money.
Activity 14
Selling surplus vegetables to the community.
Let us practice
Working in groups
- Harvest just enough vegetables to sell for the day.
- Sell the vegetables to the teachers and other staff members in the school.
- Sell the other vegetables to the community around your school.
Look at the following pictures.
A.
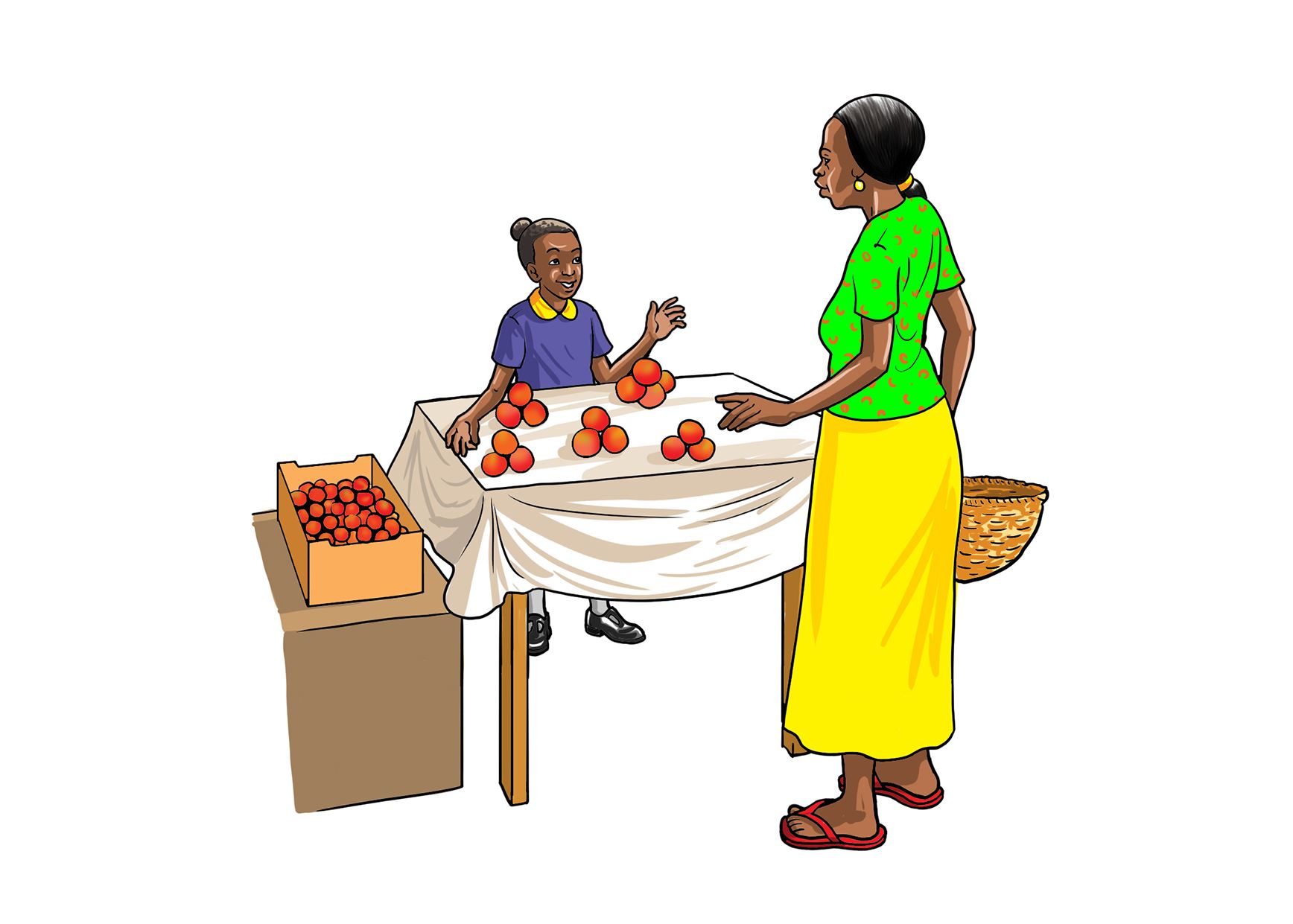

B.

Selling vegetables to the community
What activities do you observe in pictures (a) and (b)?
Share your experiences with the other groups.
Let us understand
- It is difficult to store surplus vegetables since they go bad quickly.
- When we sell surplus vegetables, we make money.
- Planning on how to use the money earned from sale helps us to be a b responsible.
Growing vegetables at home
Activity 15
Home project
Assisting parents or guardians in growing vegetables.
Let us practice at home
- Use the skills you have acquired to help your parents or guardians to grow vegetables at home.
- Help your parents or guardians to carry out the activities below:
- Prepare and grow seedlings in the nursery.
- Transplant the seedlings to a prepared piece of land, when they are ready.
- Take care of the vegetables until they are ready for haversting.
- Harvest the ready vegetables.
- Prepare vegetables for cooking and consumption.
- Sell the remaining vegetables to the local community.
- Discuss with your parents or guardians how the money earned will be spent.
Let us understand
- The knowledge we get in school can be used at home to help our parents or guardians grow vegetables.
- When we help our parents or guardians to grow vegetables at home, we get the following benefits:
- We eat nutritious foods. Vegetables give us a lot of vitamins and mineral salts.
- Eating enough vegetables prevents constipation.
- We sell the vegetables and get money to buy other foods, clothes and pay school fees.
Importance of vegetables
- Vegetables provide us with nutrition.
- Vegetables can be sold to earn income.