Getting Ready: In our learning activities, we will:
- Discuss the signs, symptoms and prevention and management of the following internal parasites:
- Jiggers
- Lice
- Mites (that cause scabies)
- Find out more about ways of preventing the spread of external parasites. We will share this information with other people in our communities. In this way, we will develop interest in ensuring good health for ourselves, our families and our communities.
What we already know
From earlier studies in Environmental Activities, Home Science and Science and Technology, we already know that it is important to take proper care of our living areas and our personal items. In what ways do we observe personal hygiene at home and in school? Discuss some of these ways with a partner.
We also know that it is important to wash fruits well before eating. It is also important to wash hands before handling foods. Why is that important? Discuss it with a friend.
Activity 2.19: Learn new words

Activity 2.20: How are external parasites spread?
Work safely in groups. Discuss these questions: What external parasites do you know? How are these parasites spread? How do they affect human beings? In which ways can we prevent their spread from one person to another?
External Parasites
Activity 2.21: What are external body parasites?
Work safely in groups. Use the Internet to find out the following:
- What are external body parasites?
- What are some examples of external body parasites?
- Where are they found in the human body?

Learn more. Grow. Share the knowledge with your family and community members
- Parasites which attack human on the outside of the body are known as external parasites.
- The affected person is known as the host.
- Jiggers, lice (head lice) and scabies mites are examples of external body parasites.
- External parasites get food and shelter from the host.
- Parasites cause harm to the host and may kill the host.
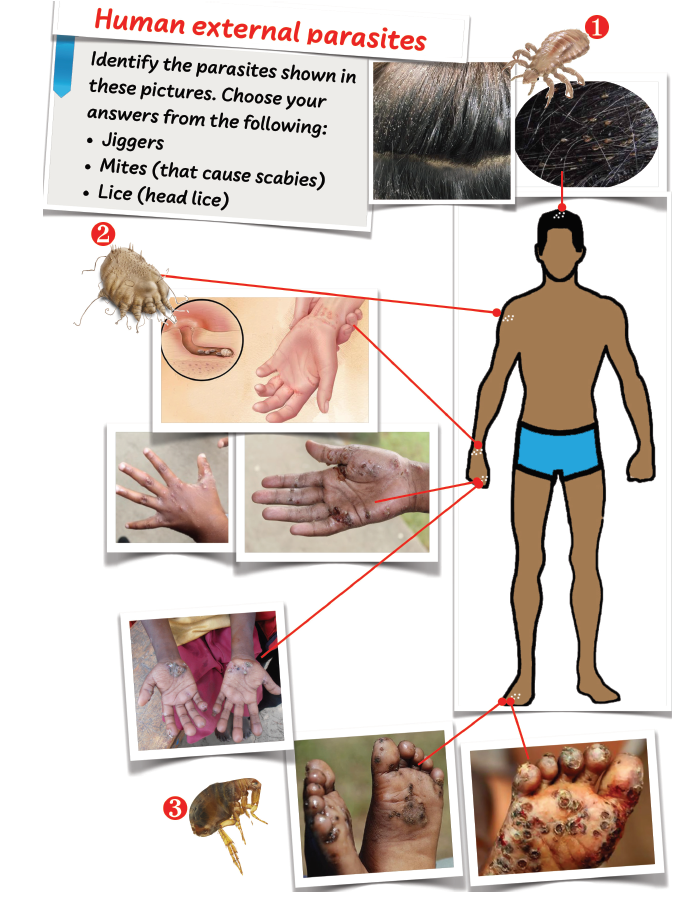
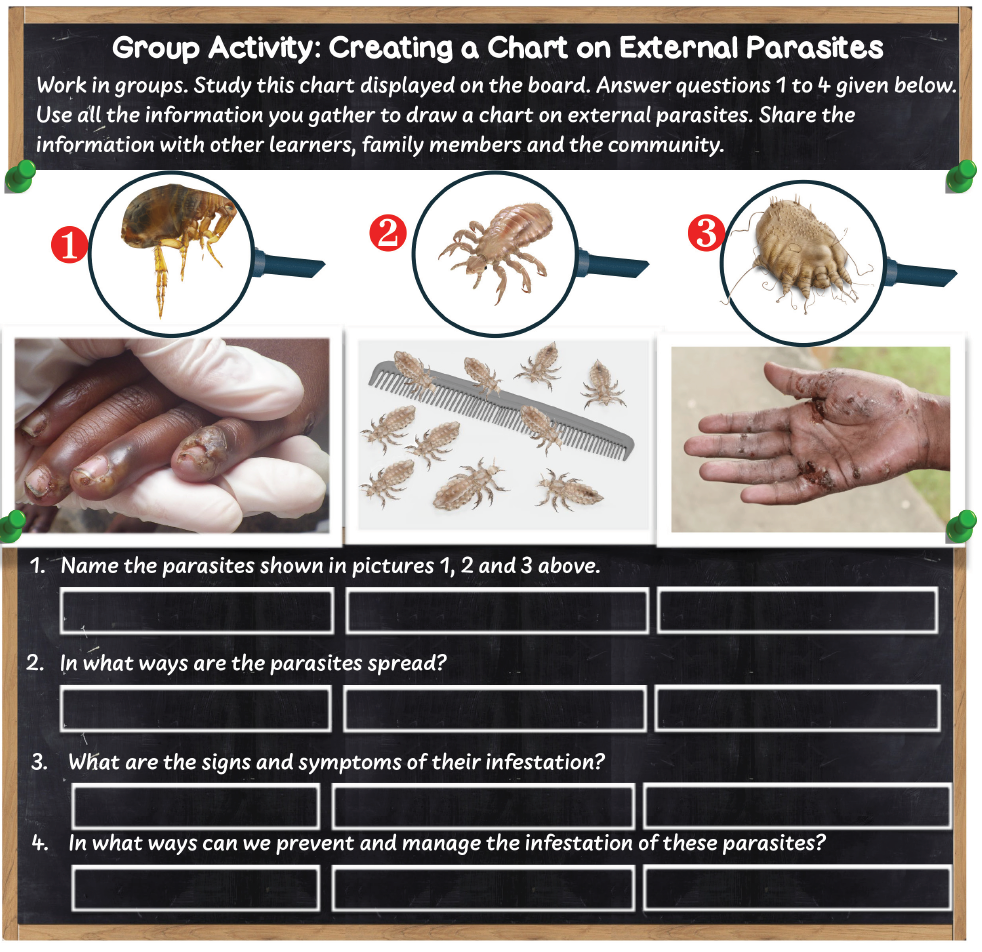
Activity 2.22: Identifying human external parasites
Work safely in groups. Identify the parasites labelled 1, 2 and 3.
Jiggers are external parasites
Activity 2.23: Let us find out more about jiggers
In groups, use the Internet safely to find out the following:
- How are jiggers spread?
- What parts of the body do jiggers attack?
- What are the signs and symptoms of jigger infestation?
- How can you protect yourself from jigger infestation?
- What are the effects of jigger infestation?
Chigger gets a jigger: Read this story
Chigger felt itchy behind one of his toes. He asked his friend, Chigoe, to look at it. He discovered a jigger. They went to the school clinic. The nurse wore his protective gloves, removed the jigger, and disinfected Chigger's feet.
Chigger wondered how he got the jigger. He and Chigoe used the Internet to find out more about jiggers. They discovered that they are little fleas that live a few centimeters under sand or soil. They are common in earthen floors. Chigger had been playing outside the dog's kennel. He was without shoes.
The adult female jigger burrows the skin leaving just the tip of the abdomen exposed. She swells as she lays eggs, making a big white sac. The jigger is seen as a swelling with a black head at the center. The jigger then bursts and releases the eggs into the environment. The eggs hatch into other fleas and the cycle begins once again.
Activity 2.24: How are jiggers spread?
Discuss these questions.
- What caused the itching in Chigger’s toe?
- What signs and symptoms of jigger infestation did Chigger show?
- Use the Internet to search for causes, signs, symptoms, prevention and control of jiggers.
- Check the meaning of the word Chigoe.
Learn more. Grow. Share the knowledge with your family and community members
Jiggers live in dirty conditions such as in soil and sand. Jiggers lay many eggs in dirty floors. You get jiggers from infested dusty areas, sandy areas and earthen floors. Jiggers cause itching. They form a large white sac.
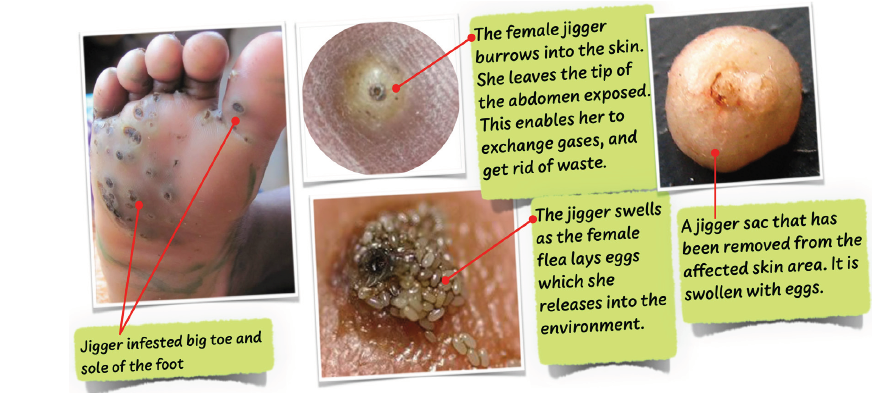
Jiggers also affect hands, knees, buttocks and other parts of the body.
To prevent jigger infestation:
- Wear shoes to prevent infection.
- Keep the environment clean.
- Sweep and wash the floors.
- Pour water on earthen floors to prevent them from laying eggs.
Read more about eradicating jiggers on the Internet.
Lice are external parasites
Activity 2.25: Let us find out more about lice
Work safely in groups. Use the Internet to find out the following:
- How is head lice spread?
- What parts of the body do lice attack?
- What are the signs, symptoms and effects of lice infestation?
- How are lice spread?
- How can you protect yourself from lice infestation?
Learn more. Grow. Share the knowledge with your family and community members
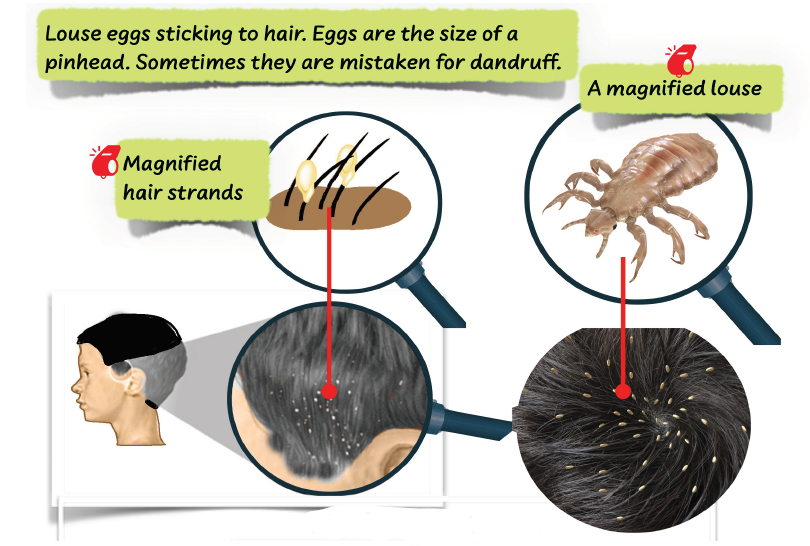
Lice are external parasites that suck the blood of the host. They are found on the hairy parts of the body such as the head where they lay their eggs. They are also found in the seams of clothes of people infested with lice.
You get lice through physical contact with infected people. You also get it through sharing combs, beds and bedding. Lice infestation causes itching. White specks are seen on the hair and mature insects are seen moving about. Lice infestation can be prevented by observing personal hygiene such as bathing regularly, keeping the hair clean, not sharing combs, and wearing clean ironed clothes.

Complete these sentences:
- Do not share to prevent the spread of lice.
- Wash your hair with to prevent the spread of lice.
Scabies mites are external parasites
Activity 2.27: Let us find out more about scabies mites
Work safely in groups. Use the Internet to find out the following:
- How are scabies mites spread?
- What parts of the body do scabies mites attack?
- What are the signs and symptoms of scabies mites infestation?
- How are scabies mites spread?
- How can you protect yourself from scabies mites infestation?
- What are the effects of scabies mites infestation? Share the information with other learners, family members and people in your community.
Learn more. Grow. Share the knowledge with your family and community members
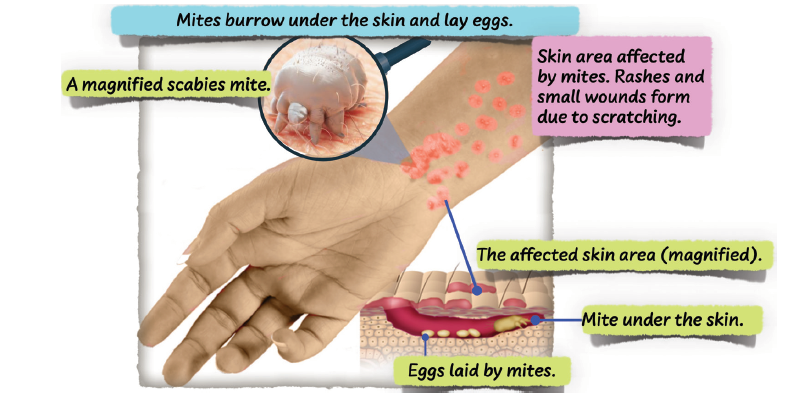
Scabies is a skin condition caused by a mite that burrows in the skin. Scabies occurs when there is:
- Physical contact with an infected person.
- Sharing of clothes with an infected person.
- Sharing of towels and bedding with an infected person.
A person with scabies feels itchy. Rashes appear on the skin. A small wound may form due to scratching. With time, a grey crust may form. Infestation from scabies mites can be prevented by:
- Not sharing clothes, socks, towels and bedding.
- Soaking clothes, towels and beddings in hot water and soap.
- Cleaning infested surfaces with hot water and soap.
- Avoiding physical contact with an infected person.
Activity 2.28: Complete this activity
Involve your family. Serve your community. Ask to find out. Learn. Share. Grow. Solve problems.
- With the guidance of your parent or guardian, clean your house and the home compound to prevent jigger infestation.
- If the floor is earthen, splash water to settle the dust.
- Help to soak and wash clothes.
- Create banners to inform people in your community on ways of preventing and managing the infestation of external parasites.
- Jiggers are common in many areas. Create messages to help prevent the spread of jiggers. Share them with people in your community.
Activity 2.29: Creating messages to prevent the spread of jiggers

Summary

Do the same. Tick columns to check your progress.
Reports from a Health Camp