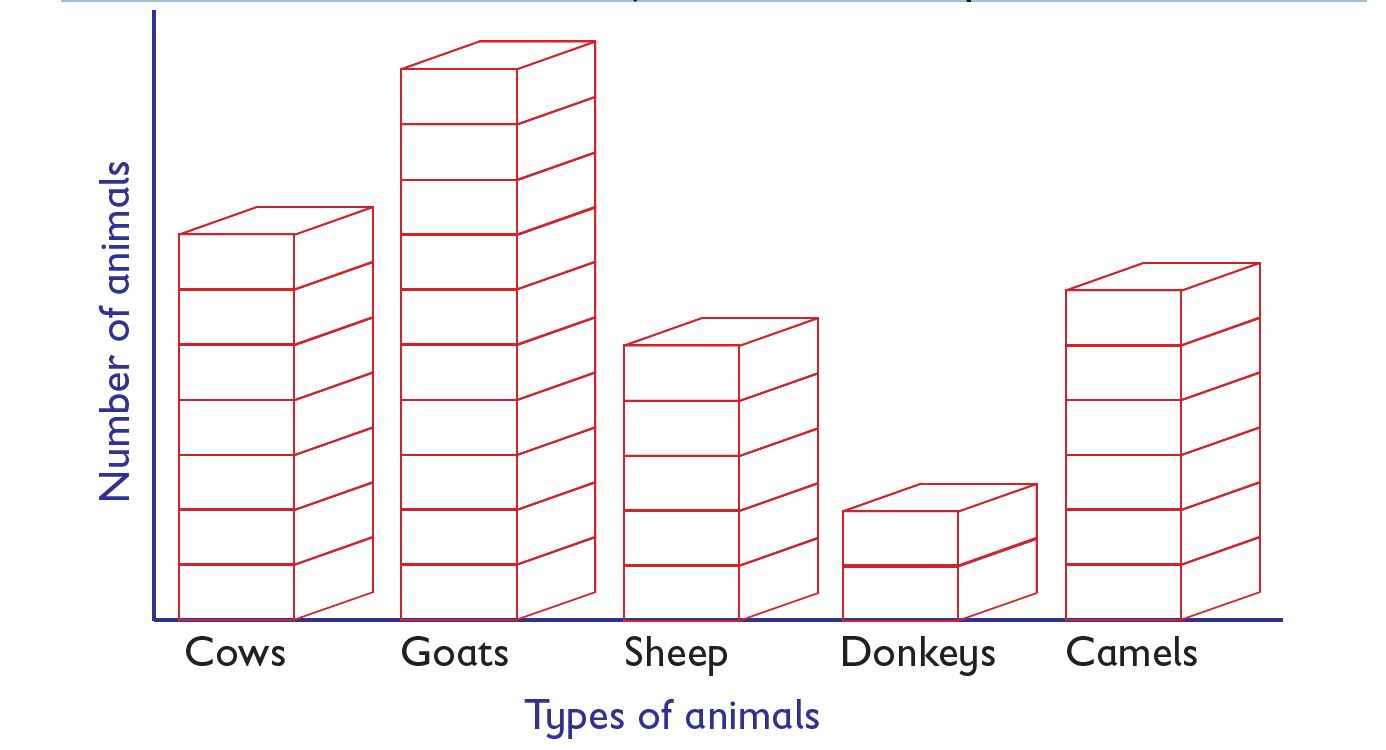
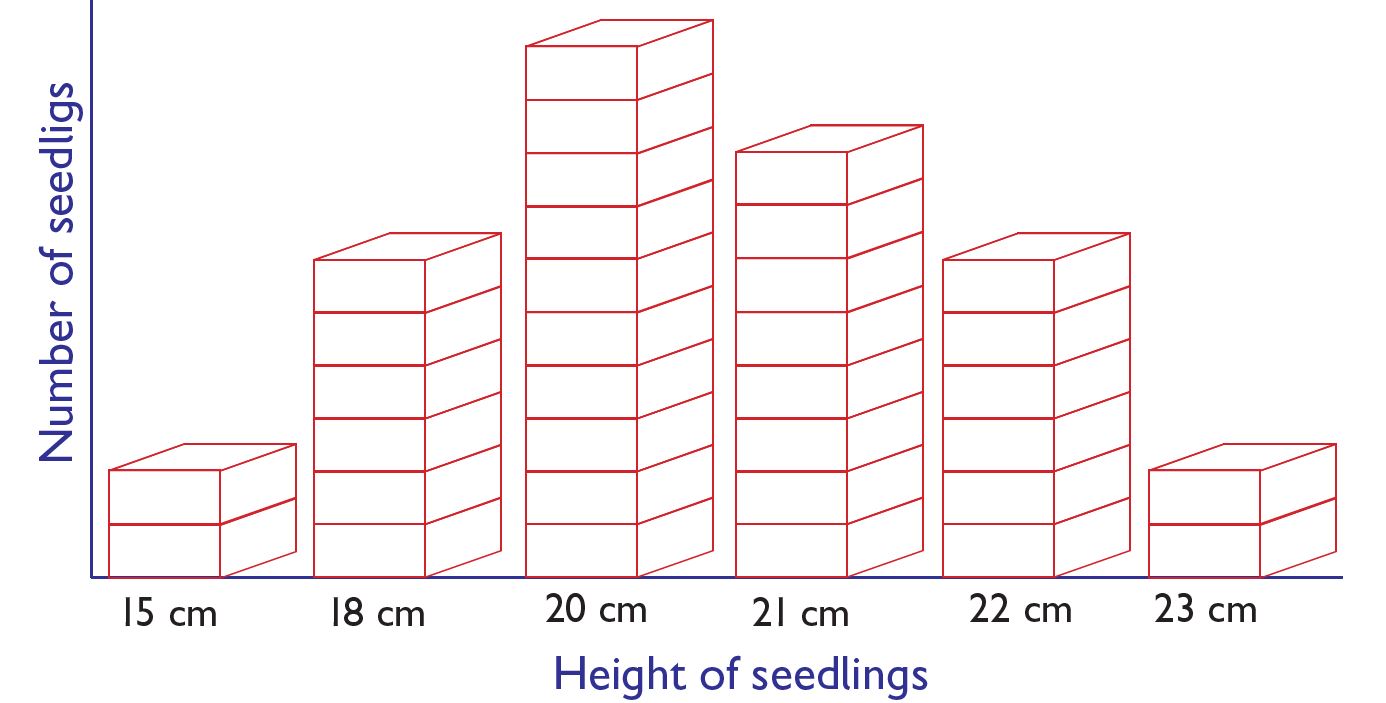
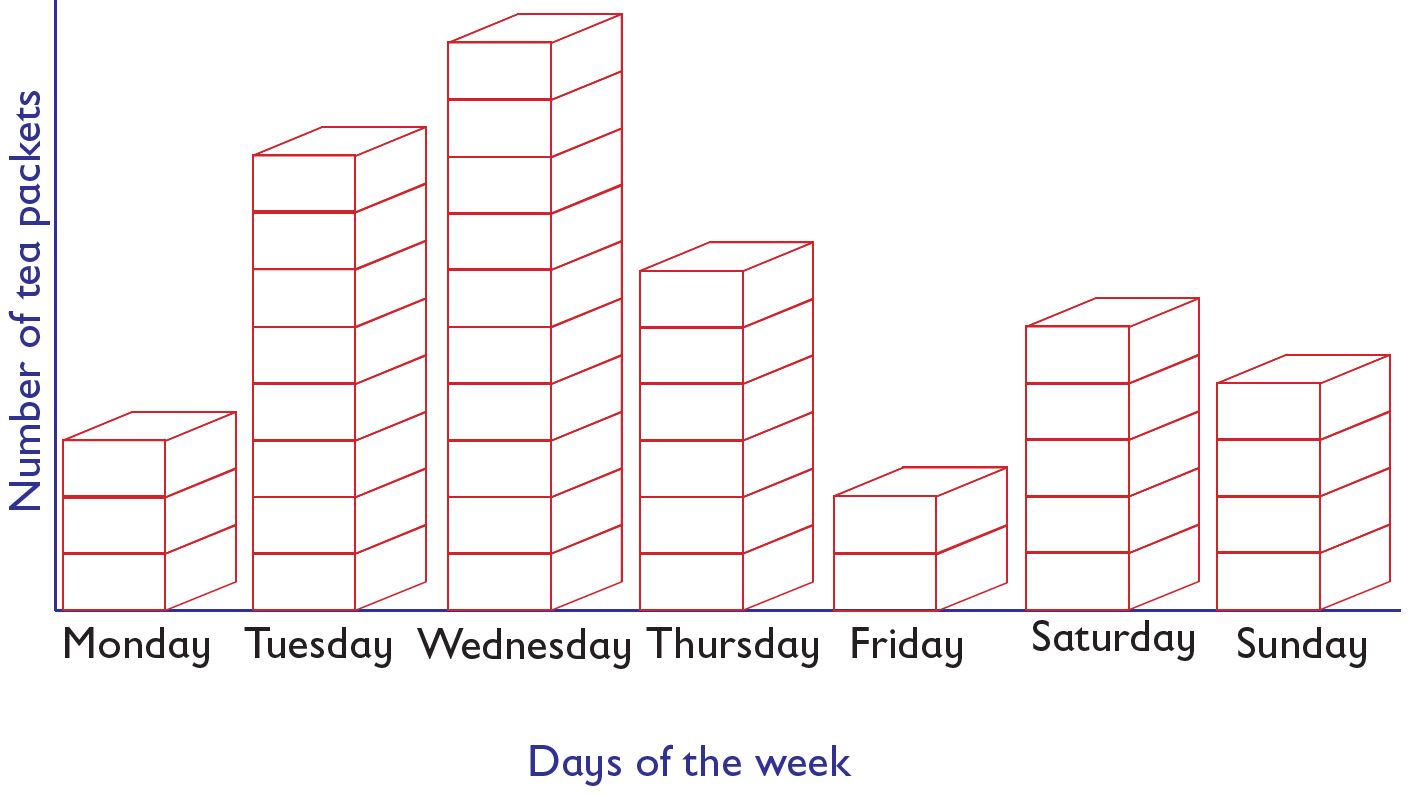
Interpretation of data represented through piling
Example 3
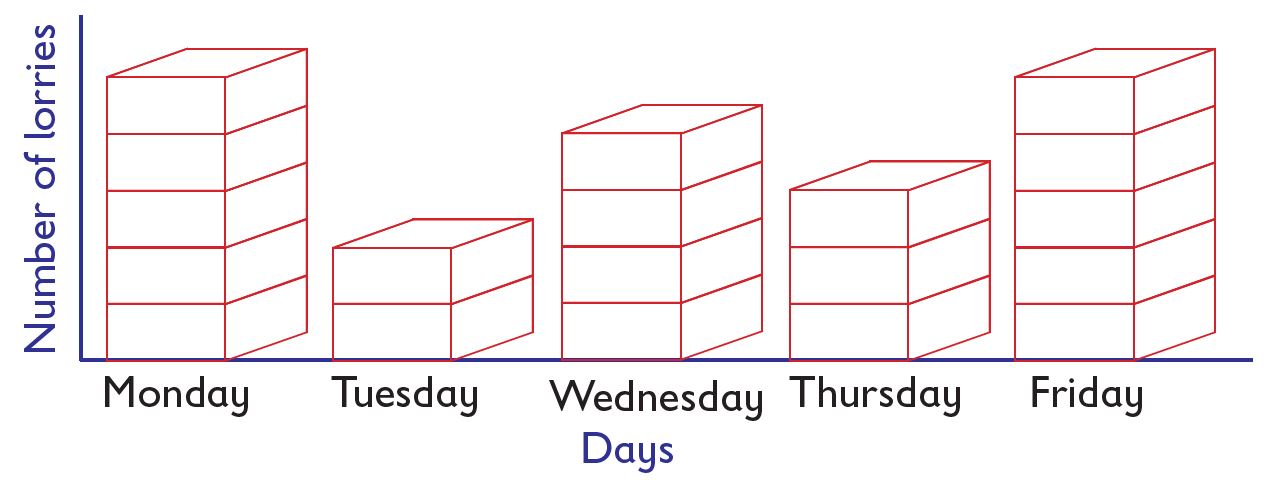
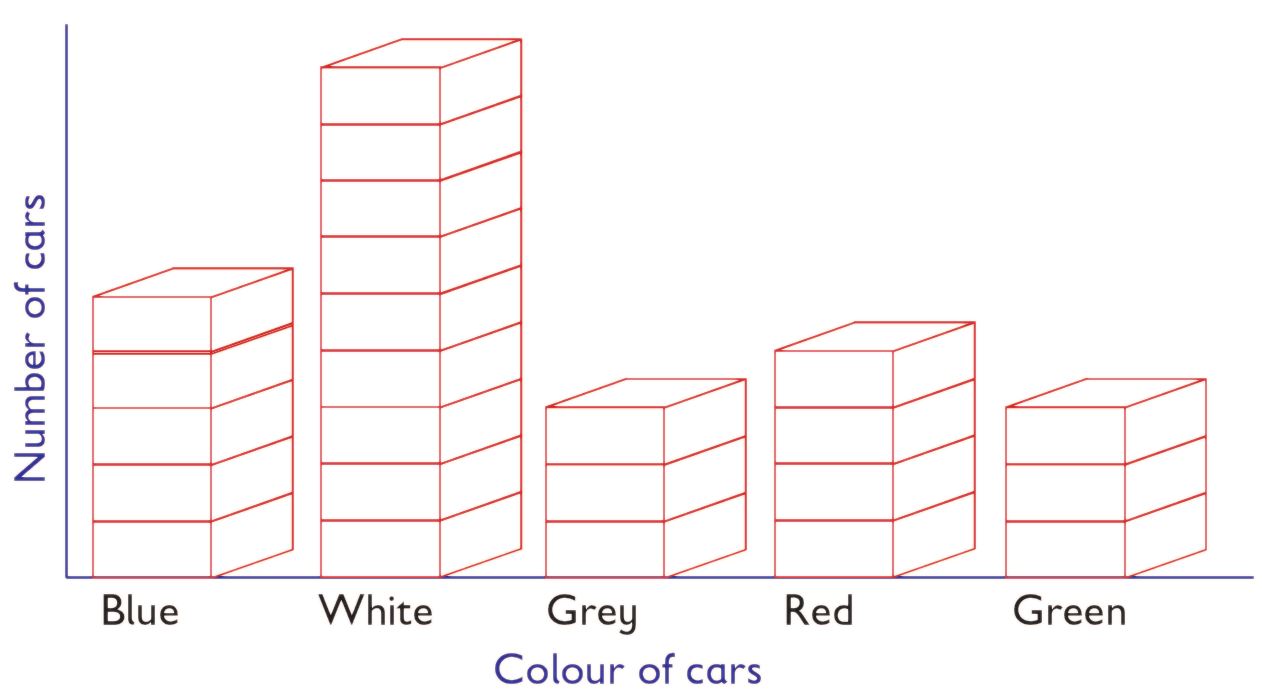
Omari and Awiti represented the colours of cars that passed by their school gate one afternoon. The information was represented using blocks of wood as shown.
Use the diagram to answer the following questions:
- How many white cars passed by the gate?
Answer. White cars were 9. - Which two colours had the same number of cars that passed by the gate?
Answer. Grey and green. - How many more blue cars than red cars passed by the gate?
Answer. Blue 5, red 4. Difference is 5 – 4 = 1 - How many vehicles passed by the school gate altogether?
Answer. Blue 5, white 9, grey 3, red 4, green 3.
Total number of cars is
5 + 9 + 3 + 4 + 3 = 24
Another example
Example 4
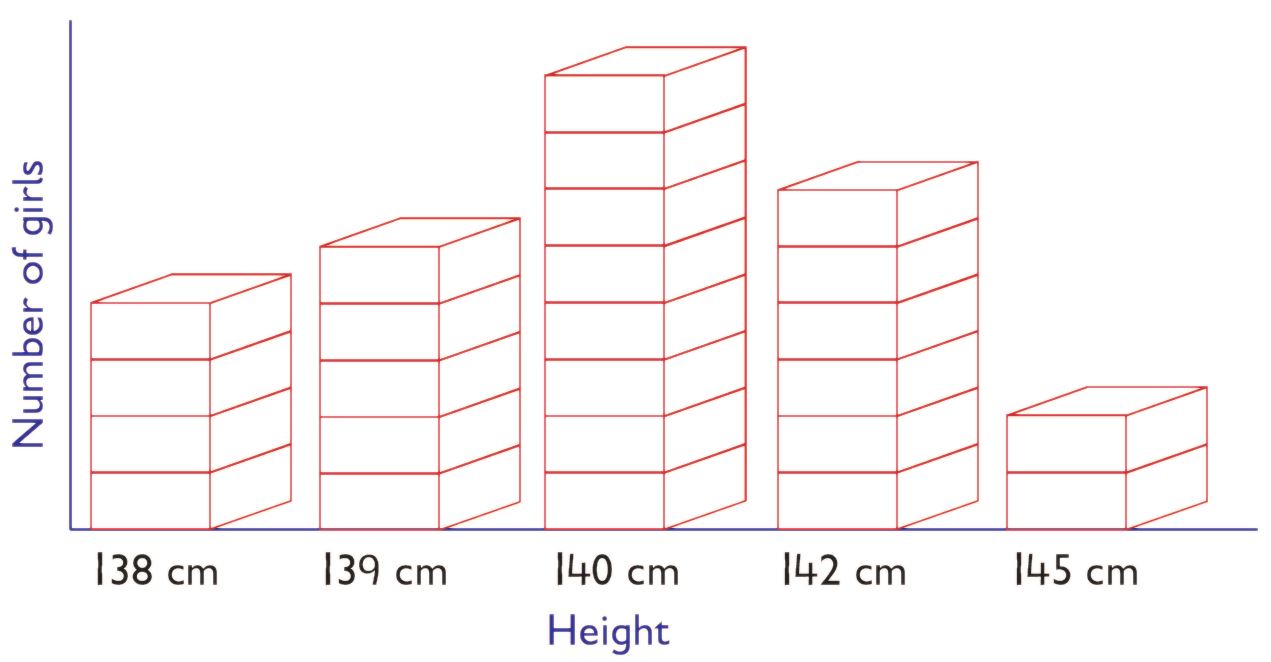
Mwadime measured the heights in centimetres of girls who played netball for Grade Five class. The results were represented as shown
Use the diagram to answer the following questions:
- Which was the most common height?
Answer. The most common height was 140 cm. - How many girls were 138 cm tall?
Answer. There were 4 girls who were 138 cm tall. - How many girls were 139 cm and 145 cm tall?
Answer
There were 5 girls who were 139 cm tall.
There were 2 girls who were 145 cm tall.
Total number of girls was 5 + 2 = 7 - How many girls were above 139 cm?
Answer
Number of girls who were 140 cm tall were 8.
Number of girls who were 142 cm tall were 6.
Number of girls who were 145 cm tall were 2.
Total number of girls were 8 + 6 + 2 = 16